Copper homeostasis dysregulation promoting cell damage and the association with liver diseases
- PMID: 37284739
- PMCID: PMC10344562
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002697
Copper homeostasis dysregulation promoting cell damage and the association with liver diseases
Abstract
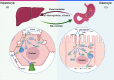
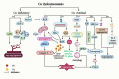
Copper plays an important role in many metabolic activities in the human body. Copper level in the human body is in a state of dynamic equilibrium. Recent research on copper metabolism has revealed that copper dyshomeostasis can cause cell damage and induce or aggravate some diseases by affecting oxidative stress, proteasome, cuprotosis, and angiogenesis. The liver plays a central role in copper metabolism in the human body. Research conducted in recent years has unraveled the relationship between copper homeostasis and liver diseases. In this paper, we review the available evidence of the mechanism by which copper dyshomeostasis promotes cell damage and the development of liver diseases, and identify the future research priorities.
Copyright © 2023 The Chinese Medical Association, produced by Wolters Kluwer, Inc. under the CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Tsang T, Davis CI, Brady DC. Copper biology. Curr Biol 2021; 31: R421–r427. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.03.054. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Jiang Y, Shi H, Peng Y, Fan X, Li C. The molecular mechanisms of copper metabolism and its roles in human diseases. Pflugers Arch 2020; 472: 1415–1429. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02412-2. - PubMed
-
- Vetlényi E, Rácz G. The physiological function of copper, the etiological role of copper excess and deficiency (in Hungarian). Orv Hetil 2020; 161: 1488–1496. doi: 10.1556/650.2020.31854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

