Genetic analysis and natural history of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease CMTX1 due to GJB1 variants
- PMID: 37284795
- PMCID: PMC10545504
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awad187
Genetic analysis and natural history of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease CMTX1 due to GJB1 variants
Abstract
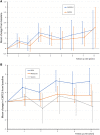
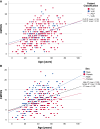
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) due to GJB1 variants (CMTX1) is the second most common form of CMT. It is an X-linked disorder characterized by progressive sensory and motor neuropathy with males affected more severely than females. Many reported GJB1 variants remain classified as variants of uncertain significance (VUS). In this large, international, multicentre study we prospectively collected demographic, clinical and genetic data on patients with CMT associated with GJB1 variants. Pathogenicity for each variant was defined using adapted American College of Medical Genetics criteria. Baseline and longitudinal analyses were conducted to study genotype-phenotype correlations, to calculate longitudinal change using the CMT Examination Score (CMTES), to compare males versus females, and pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants versus VUS. We present 387 patients from 295 families harbouring 154 variants in GJB1. Of these, 319 patients (82.4%) were deemed to have P/LP variants, 65 had VUS (16.8%) and three benign variants (0.8%; excluded from analysis); an increased proportion of patients with P/LP variants compared with using ClinVar's classification (74.6%). Male patients (166/319, 52.0%, P/LP only) were more severely affected at baseline. Baseline measures in patients with P/LP variants and VUS showed no significant differences, and regression analysis suggested the disease groups were near identical at baseline. Genotype-phenotype analysis suggested c.-17G>A produces the most severe phenotype of the five most common variants, and missense variants in the intracellular domain are less severe than other domains. Progression of disease was seen with increasing CMTES over time up to 8 years follow-up. Standard response mean (SRM), a measure of outcome responsiveness, peaked at 3 years with moderate responsiveness [change in CMTES (ΔCMTES) = 1.3 ± 2.6, P = 0.00016, SRM = 0.50]. Males and females progressed similarly up to 8 years, but baseline regression analysis suggested that over a longer period, females progress more slowly. Progression was most pronounced for mild phenotypes (CMTES = 0-7; 3-year ΔCMTES = 2.3 ± 2.5, P = 0.001, SRM = 0.90). Enhanced variant interpretation has yielded an increased proportion of GJB1 variants classified as P/LP and will aid future variant interpretation in this gene. Baseline and longitudinal analysis of this large cohort of CMTX1 patients describes the natural history of the disease including the rate of progression; CMTES showed moderate responsiveness for the whole group at 3 years and higher responsiveness for the mild group at 3, 4 and 5 years. These results have implications for patient selection for upcoming clinical trials.
Keywords: ACGS; ACMG; CMT1X; Cx32; connexin 32.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
M.M.R. consults for Alnylam, Eido, Augustine Therapeutics, and DTx Pharma. In the last 3 years, S.S.S. has served on the Scientific Advisory Board for Mitochondria in Motion and Disarm Therapeutics, and consulted for Pfizer, Applied Therapeutics, Passage Bio, and Toray Industries. J.B. receives consulting fees, honoraria or expense reimbursement from Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University Thailand, Charcot Marie Tooth Association USA, National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Applied Therapeutics, DTx Pharma, Hereditary Neuropathy Foundation. S.R. is currently an employee of the Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson. The work submitted represents research conducted while she was at Wayne State University. D.N.H. has served as a consultant or on a Scientific Advisory Board for Regenacy, Pfizer, Passage Bio, Applied Therapeutics, DTXx Pharma, Sarepta, Neurogene, Swan Bio, GLG and Guidepoint Global. In the past 3 years, D.P. has served on Clinical Advisory Board for Arvinas, Augustine Tx, DTx Pharma. M.D.W. has received honoraria for serving on Scientific Advisory Boards for Alexion, UCB-Ra, Argenx, Biogen, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Amylyx and speaker honoraria from Soleo Health.
Figures

References
-
- Shy ME, Siskind C, Swan ER, et al. CMT1X Phenotypes represent loss of GJB1 gene function. Neurology. 2007;68:849–855. - PubMed
-
- Siskind CE, Murphy SM, Ovens R, Polke J, Reilly MM, Shy ME. Phenotype expression in women with CMT1X. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2011;16:102–107. - PubMed
-
- Yiu EM, Geevasinga N, Nicholson GA, Fagan ER, Ryan MM, Ouvrier RA. A retrospective review of X-linked charcot-marie-tooth disease in childhood. Neurology. 2011;76:461–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

