Broadly neutralizing antibodies against COVID-19
- PMID: 37285620
- PMCID: PMC10301462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2023.101332
Broadly neutralizing antibodies against COVID-19
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 has led to hundreds of millions of infections and millions of deaths, however, human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) can be an effective treatment. Since SARS-CoV-2 emerged, a variety of strains have acquired increasing numbers of mutations to gain increased transmissibility and escape from the immune response. Most reported neutralizing human mAbs, including all approved therapeutic ones, have been knocked down or out by these mutations. Broadly neutralizing mAbs are therefore of great value, to treat current and possible future variants. Here, we review four types of neutralizing mAbs against the spike protein with broad potency against previously and currently circulating variants. These mAbs target the receptor-binding domain, the subdomain 1, the stem helix, or the fusion peptide. Understanding how these mAbs retain potency in the face of mutational change could guide future development of therapeutic antibodies and vaccines.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Oxford University holds intellectual property related to SARS-CoV-2 mAbs discovered in Gavin R Screaton’s laboratory and DIS consults for AstraZeneca
Figures
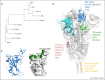


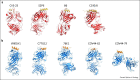
References
-
- Liu L., et al. Potent neutralizing antibodies against multiple epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 spike. Nature. 2020;584:450–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

