Antagonistic circuits mediating infanticide and maternal care in female mice
- PMID: 37286598
- PMCID: PMC10648307
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06147-9
Antagonistic circuits mediating infanticide and maternal care in female mice
Abstract
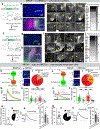
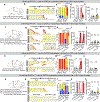
In many species, including mice, female animals show markedly different pup-directed behaviours based on their reproductive state1,2. Naive wild female mice often kill pups, while lactating female mice are dedicated to pup caring3,4. The neural mechanisms that mediate infanticide and its switch to maternal behaviours during motherhood remain unclear. Here, on the basis of the hypothesis that maternal and infanticidal behaviours are supported by distinct and competing neural circuits5,6, we use the medial preoptic area (MPOA), a key site for maternal behaviours7-11, as a starting point and identify three MPOA-connected brain regions that drive differential negative pup-directed behaviours. Functional manipulation and in vivo recording reveal that oestrogen receptor α (ESR1)-expressing cells in the principal nucleus of the bed nucleus of stria terminalis (BNSTprESR1) are necessary, sufficient and naturally activated during infanticide in female mice. MPOAESR1 and BNSTprESR1 neurons form reciprocal inhibition to control the balance between positive and negative infant-directed behaviours. During motherhood, MPOAESR1 and BNSTprESR1 cells change their excitability in opposite directions, supporting a marked switch of female behaviours towards the young.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Statement of competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Parmigiani S & vom Saal F Infanticide And Parental Care. (2016).
-
- Soroker V & Terkel J Changes in incidence of infanticidal and parental responses during the reproductive cycle in male and female wild mice Mus musculus. Animal Behaviour 36, 1275–1281 (1988).
-
- McCarthy MM & vom Saal FS The influence of reproductive state on infanticide by wild female house mice (Mus musculus). Physiology & behavior 35, 843–849 (1985). - PubMed
Method-only references
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

