Alectinib for treating patients with metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC: systematic review and network metanalysis
- PMID: 37287941
- PMCID: PMC10242442
- DOI: 10.2217/lmt-2022-0018
Alectinib for treating patients with metastatic ALK-positive NSCLC: systematic review and network metanalysis
Abstract
Aim: To compare the efficacy and safety of alectinib with other ALK inhibitors in treating patients with metastatic or locally advanced ALK-positive NSCLC.
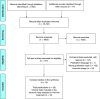
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted up to November 2021. Network meta-analyses were performed using the frequentist method (random effects). GRADE evidence profile was conducted.
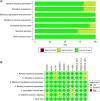
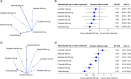
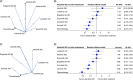
Results: 13 RCTs were selected. For overall survival, alectinib was found to reduce the risk of death compared with crizotinib. In progression-free survival, alectinib reduced the risk of death or progression compared with crizotinib and ceritinib. Subgroup analysis by brain metastasis at baseline showed the superiority of alectinib over crizotinib and a similar effect compared with second-and third-generation inhibitors. Alectinib showed a good safety profile compared with the other ALK inhibitors.
Keywords: anaplastic lymphoma kinase; carcinoma; neoplasm metastasis; network meta-analysis; non-small-cell lung.
Plain language summary
This article reports the results of a systematic literature review with network meta-analysis (NMA) that aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of alectinib with other ALK inhibitors in treating patients with metastatic or locally advanced ALK-positive NSCLC. The results show that alectinib reduces the risk of death and the risk of progression compared with crizotinib. For progression-free survival, further significant reductions were observed when compared with ceritinib. For the other ALK inhibitors, no statistically significant differences were found. Subgroup analysis according to the presence of CNS metastases at baseline were consistent in showing the superiority of alectinib over crizotinib and the absence of statistically significant differences compared with second-and third-generation inhibitors. Alectinib showed a good safety profile compared with the other ALK inhibitors, reducing the frequency of adverse events (AEs) compared with ceritinib, and with no statistically significant differences compared with lorlatinib, brigatinib, ensartinib and crizotinib for the frequency of serious AEs or discontinuation of treatment due to AEs. The results of this study suggest clinically relevant insights in decision-making based on patient survival and progression-free survival. Furthermore, considering the importance of reducing the risk of intracranial progression and the need for available therapies for patients who will inevitably progress, alectinib could be considered as a first-line treatment for patients with ALK-positive NSCLC.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Bayesian network meta-analysis of ALK inhibitor treatments in patients with ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2023 Aug;12(15):15983-15997. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6241. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37334877 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of alectinib versus crizotinib on progression-free survival, central nervous system efficacy and adverse events in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med. 2020 Jul;9(4):1782-1796. doi: 10.21037/apm-19-643. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Ann Palliat Med. 2020. PMID: 32527124
-
Efficacy and Safety of First-Line Treatment Strategies for Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 8;11:754768. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.754768. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34820326 Free PMC article.
-
ALTA-2: Phase II study of brigatinib in patients with ALK-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer who progressed on alectinib or ceritinib.Future Oncol. 2021 May;17(14):1709-1719. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-1119. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Future Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33569983
-
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Brigatinib in First-Line Treatments for Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Indirect Treatment Comparison.J Clin Med. 2022 May 24;11(11):2963. doi: 10.3390/jcm11112963. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35683354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
First case report of a novel KIF13A-ALK fusion in a lung adenocarcinoma patient and response to alectinib with a 4-year follow-up.Front Genet. 2023 Dec 13;14:1289346. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1289346. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38155713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Cancer Observatory: Lung Cancer Today (2022). https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/15-Lung-fact-sheet.pdf
-
- Ministerio De Salud Y Protección Social Departamento Administrativo De Ciencia Tecnología E Innovación–Colciencias. Guía de Práctica Clínica para para la detección temprana, diagnóstico, estadificación y tratamiento del cáncer de pulmón. Guí a No. GPC 2014 – 36. Ministerio De Salud Y Protección Social Departamento Administrativo De Ciencia Tecnología E Innovación– Colciencias, Bogotá, Colombia: (2014).
-
- Tasas de supervivencia del cáncer de pulmón (2021). www.cancer.org/es/cancer/cancer-de-pulmon/deteccion-diagnostico-clasific...
-
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Cáncer de pulmón de células no pequeñas: estadísticas (2021). www.cancer.net/es/tipos-de-cancer/cancer-de-pulmon-de-celulas-no-pequena...
-
- Dorward DA, Walsh K, Oniscu A, Wallace WA. Molecular pathology of non-small cell lung cancer. Diagnostic histopathology 23(10), 450–457 (2017).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
