Cardiotoxicity in autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 37287946
- PMCID: PMC10242691
- DOI: 10.1177/23971983221145639
Cardiotoxicity in autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for systemic sclerosis
Abstract
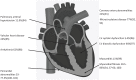
Autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation is now well-established as an effective treatment for severe systemic sclerosis with clear demonstration of favourable end-organ and survival outcomes. Treatment-related cardiotoxicity remains the predominant safety concern and contraindicates autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with severe cardiopulmonary disease. In this review, we describe the cardiovascular outcomes of autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients, discuss the potential mechanisms of cardiotoxicity and propose future mitigating strategies.
Keywords: Scleroderma; autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation; cardiac; safety; stem cell transplantation; systemic sclerosis; toxicity.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Burt RK, Shah SJ, Dill K, et al. Autologous non-myeloablative haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation compared with pulse cyclophosphamide once per month for systemic sclerosis (ASSIST): an open-label, randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet 2011; 378(9790): 498–506. - PubMed
-
- Van Laar JM, Farge D, Sont JK, et al. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation vs intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014; 311(24): 2490–2498. - PubMed
-
- Higashitani K, Takase-Minegishi K, Yoshimi R, et al. Benefits and risks of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for systemic sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mod Rheumatol 2022; 2022: roac026. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
