Biofriendly micro/nanomotors operating on biocatalysis: from natural to biological environments
- PMID: 37288308
- PMCID: PMC10240795
- DOI: 10.1007/s41048-020-00119-6
Biofriendly micro/nanomotors operating on biocatalysis: from natural to biological environments
Abstract
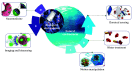
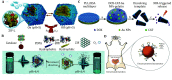
Micro/nanomotors (MNMs) are tiny motorized objects that can autonomously navigate in complex fluidic environments under the influence of an appropriate source of energy. Internal energy driven MNMs are composed of certain reactive materials that are capable of converting chemical energy from the surroundings into kinetic energy. Recent advances in smart nanomaterials design and processing have endowed the internal energy driven MNMs with different geometrical designs and various mechanisms of locomotion, with remarkable travelling speed in diverse environments ranging from environmental water to complex body fluids. Among the different design principals, MNM systems that operate from biocatalysis possess biofriendly components, efficient energy conversion, and mild working condition, exhibiting a potential of stepping out of the proof-of-concept phase for addressing many real-life environmental and biotechnological challenges. The biofriendliness of MNMs should not only be considered for in vivo drug delivery but also for environmental remediation and chemical sensing that only environmentally friendly intermediates and degraded products are generated. This review aims to provide an overview of the recent advances in biofriendly MNM design using biocatalysis as the predominant driving force, towards practical applications in biotechnology and environmental technology.
Keywords: Biocatalysis; Biofriendly MNM design; Micro/nanomotors (MNMs).
Copyright 2020 Biophysics Reports.
Conflict of interest statement
Ziyi Guo, Jian Liu, Da-Wei Wang, Jiangtao Xu and Kang Liang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chen C, He Z, Wu J, Zhang X, Xia Q, Ju H Motion of enzyme-powered microshell motors. Chem Asian J. 2019;14(14):2491–2496. - PubMed
-
- Choi H, Cho SH, Hahn SK Urease-powered polydopamine nanomotors for intravesical therapy of bladder diseases. ACS Nano. 2020;14(6):6683–6692. - PubMed
-
-
Coopersmith KJ (2017) Putting nanoparticles to work: self-propelled inorganic micro- and nanomotors. In: Hunyadi Murph SE, Larsen GK, Coopersmith KJ (eds). Book. Anisotropic and shape-selective nanomaterials. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 153−168
-
-
- Cross RA Molecular motors: the natural economy of kinesin. Curr Biol. 1997;7(10):R631–R633. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
