Predictive Value of the Changes in Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio for Outcomes After Off-Pump Coronary Surgery
- PMID: 37288449
- PMCID: PMC10243358
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S411057
Predictive Value of the Changes in Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio for Outcomes After Off-Pump Coronary Surgery
Abstract
Purpose: The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is an extensively analyzed prognostic inflammatory index in cardiac patients. The degree of change in NLR values before and after surgery (delta-NLR) can represent the inflammatory response induced by surgery and serve as a meaningful prognostic biomarker in surgical patients; however, this has not been well investigated. We aimed to investigate the predictive value of the perioperative NLR and delta-NLR for outcomes of off-pump coronary artery bypass (OPCAB) surgery by evaluating "days alive and out of hospital (DAOH)", a novel patient-centered outcome.
Patients and methods: In this single-center retrospective study, perioperative data, including NLR data, from 1322 patients were analyzed. The primary endpoint was DOAH at 90 days postoperatively (DAOH 90), and the secondary endpoint was long-term mortality. Linear regression analysis and Cox regression analysis were performed to identify independent risk factors for the endpoints. In addition, Kaplan-Meier survival curves were plotted to assess long-term mortality.
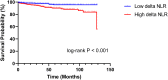
Results: The median NLR values significantly increased from 2.2 (1.6-3.1) at baseline to 7.4 (5.4-10.3) postoperatively, with median delta-NLR values of 5.0 (3.2-7.6). Preoperative NLR and delta-NLR were independent risk factors for short DAOH 90 in the linear regression analysis. In Cox regression analysis, delta-NLR, but not preoperative NLR, was an independent risk factor for long-term mortality. When patients were divided into two groups according to delta-NLR, the high delta-NLR group had a shorter DAOH 90 than the low delta-NLR group. Kaplan-Meier curves showed higher long-term mortality in the high delta-NLR group than in the low delta-NLR group.
Conclusion: In OPCAB patients, preoperative NLR and delta-NLR were significantly associated with DAOH 90, and delta-NLR was an independent risk factor for long-term mortality, indicating their role in risk assessment, which is essential for perioperative management.
Keywords: days alive and out of hospital; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; off-pump coronary artery bypass.
© 2023 Bae et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

