Interaction of Teleost Fish TRPV4 with DEAD Box RNA Helicase 1 Regulates Iridovirus Replication
- PMID: 37289063
- PMCID: PMC10308943
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00495-23
Interaction of Teleost Fish TRPV4 with DEAD Box RNA Helicase 1 Regulates Iridovirus Replication
Abstract
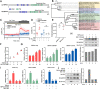
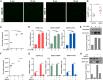
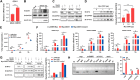
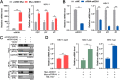
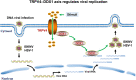
Viral diseases are a significant risk to the aquaculture industry. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) has been reported to be involved in regulating viral activity in mammals, but its regulatory effect on viruses in teleost fish remains unknown. Here, the role of the TRPV4-DEAD box RNA helicase 1 (DDX1) axis in viral infection was investigated in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Our results showed that TRPV4 activation mediates Ca2+ influx and facilitates infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV) replication, whereas this promotion was nearly eliminated by an M709D mutation in TRPV4, a channel Ca2+ permeability mutant. The concentration of cellular Ca2+ increased during ISKNV infection, and Ca2+ was critical for viral replication. TRPV4 interacted with DDX1, and the interaction was mediated primarily by the N-terminal domain (NTD) of TRPV4 and the C-terminal domain (CTD) of DDX1. This interaction was attenuated by TRPV4 activation, thereby enhancing ISKNV replication. DDX1 could bind to viral mRNAs and facilitate ISKNV replication, which required the ATPase/helicase activity of DDX1. Furthermore, the TRPV4-DDX1 axis was verified to regulate herpes simplex virus 1 replication in mammalian cells. These results suggested that the TRPV4-DDX1 axis plays an important role in viral replication. Our work provides a novel molecular mechanism for host involvement in viral regulation, which would be of benefit for new insights into the prevention and control of aquaculture diseases. IMPORTANCE In 2020, global aquaculture production reached a record of 122.6 million tons, with a total value of $281.5 billion. Meanwhile, frequent outbreaks of viral diseases have occurred in aquaculture, and about 10% of farmed aquatic animal production has been lost to infectious diseases, resulting in more than $10 billion in economic losses every year. Therefore, an understanding of the potential molecular mechanism of how aquatic organisms respond to and regulate viral replication is of great significance. Our study suggested that TRPV4 enables Ca2+ influx and interactions with DDX1 to collectively promote ISKNV replication, providing novel insights into the roles of the TRPV4-DDX1 axis in regulating the proviral effect of DDX1. This advances our understanding of viral disease outbreaks and would be of benefit for studies on preventing aquatic viral diseases.
Keywords: Ca2+; DDX1; HSV-1; ISKNV; TRPV4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Galindo-Villegas J, Montalban-Arques A, Liarte S, de Oliveira S, Pardo-Pastor C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Meseguer J, Valverde MA, Mulero V. 2016. TRPV4-mediated detection of hyposmotic stress by skin keratinocytes activates developmental immunity. J Immunol 196:738–749. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501729. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

