[CT technology: photon-counting detector computed tomography]
- PMID: 37289254
- PMCID: PMC10248982
- DOI: 10.1007/s00117-023-01166-z
[CT technology: photon-counting detector computed tomography]
Abstract
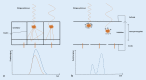
Background: Photon-counting detector computed tomography (PCD-CT) is a CT technology that overcomes many limitations of conventional detectors. Direct conversion of photons hitting the detector into electrical signals combined with more sensitive and accurate photon detection simultaneously allows spectral evaluation and also potential reduction in radiation exposure to the patient. The combination of energy thresholds and elimination of detector septa allows for a reduction of electronic noise, an increase of spatial resolution, and an improvement of dose efficiency.
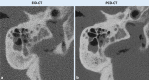
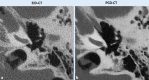
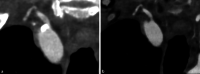
Achievements: Recent research has confirmed significantly reduced image noise, reduced radiation dose, increased spatial resolution, improved iodine signal, and a reduction in artifacts. Spectral imaging potentiates these effects and also allows retrospective calculation of virtual monoenergetic images, virtual noncontrast images or iodine maps. Thus, the photon-counting technique offers the possibility of using various contrast agents, with the prospect of single-scan multiphase imaging or visualization of specific metabolic processes. Therefore, further research and complementary approval processes are necessary for clinical application. Likewise, further research is needed to develop and validate optimal settings and reconstructions for a wide variety of situations, as well as to test new application possibilities.
Conclusions: The only photon-counting detector CT device available on the market to date received clinical approval in 2021. It remains to be seen which other applications will become possible through improvements in hardware and software. This technology has already demonstrated an impressive superiority compared with the current standard of CT imaging, especially regarding high-resolution imaging of detailed structures and examinations with high radiation exposure.
Zusammenfassung: HINTERGRUND: Die photonenzählende Computertomographie („photon-counting detector computed tomography“, PCD-CT) ist eine Technologie, die viele Einschränkungen der herkömmlichen Detektoren überwindet. Eine direkte Umwandlung der auf den Detektor eintreffenden Photonen in elektrische Signale, verbunden mit einer sensitiveren und präziseren Photonerfassung ermöglicht eine spektrale Auswertung sowie eine potenziell verringerte Strahlenexposition des Patienten. Durch die Kombination von angewandten Energieschwellenwerten und den Verzicht auf Detektorsepten kann elektronisches Rauschen reduziert, die Ortsauflösung erhöht und die Dosiseffizienz gesteigert werden.
Bewertung: Aktuelle Forschungsarbeiten bestätigen deutlich reduziertes Bildrauschen, reduzierte Strahlendosis, erhöhte Ortsauflösung, verbessertes Jodsignal sowie eine Reduktion von Artefakten. Die spektrale Auswertung potenziert diese Effekte und ermöglicht auch retrospektiv die Errechnung virtuell-monoenergetischer Bilder, virtuell-nativer Bilder oder Jodkarten. Perspektivisch ergibt sich durch die photonenzählende Technologie die Möglichkeit zur Anwendung diverser Kontrastmittel, mit der Aussicht auf einzeitige Mehrphasenbildgebung oder zur Visualisierung bestimmter Stoffwechselprozesse. Bis zum klinischen Einsatz sind hierzu weitere Grundlagenforschung sowie ergänzende Zulassungsprozesse notwendig.
Schlussfolgerung: Das bisher einzige am Markt verfügbare PCD-CT-Gerät erhielt 2021 die Zulassung. Es bleibt abzuwarten, welche weitere Anwendungen durch Verbesserungen von Hardware und Software möglich werden. Insbesondere für hochauflösende Bildgebung bei detaillierten Fragestellungen und Untersuchungen mit hoher Strahlenbelastung zeigt die Technologie bereits heute eine eindrucksvolle Überlegenheit gegenüber dem vorherigen Technologiestandard.
Keywords: Imaging quality; Photon-counting detectors; Radiation dosage; Spatial resolution; Spectral imaging.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Medizin Verlag GmbH, ein Teil von Springer Nature.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical