Roles and Effects of Interferon Lambda Signaling in the Context of Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 37289801
- PMCID: PMC10517327
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2023.0037
Roles and Effects of Interferon Lambda Signaling in the Context of Bacterial Infections
Abstract
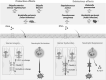
Type III interferon, or interferon lambda (IFNλ), was discovered 20 years ago and has been studied primarily for its role in combatting viral infections. However, it is also induced in response to certain bacterial infections but its roles and effects in this context are relatively poorly understood. In this mini review, we discuss the roles of IFNλ signaling in bacterial infections, highlighting its deleterious or protective effects for different infections. We also discuss a couple of recent studies showing that some bacteria possess defense mechanisms against the effects of IFNλ. We hope that this review will spur further investigation into the roles of IFNλ in the context of bacterial infections and will promote considerations of its therapeutic potential for these infections.
Keywords: bacterial infection; innate immunity; interferon lambda; intestinal infection; respiratory infection; type III interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

