Imaging Early Life Cardiovascular Phenotype
- PMID: 37289903
- PMCID: PMC10501740
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322054
Imaging Early Life Cardiovascular Phenotype
Abstract
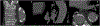
The growing epidemics of obesity, hypertension, and diabetes, in addition to worsening environmental factors such as air pollution, water scarcity, and climate change, have fueled the continuously increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). This has caused a markedly increasing burden of CVDs that includes mortality and morbidity worldwide. Identification of subclinical CVD before overt symptoms can lead to earlier deployment of preventative pharmacological and nonpharmacologic strategies. In this regard, noninvasive imaging techniques play a significant role in identifying early CVD phenotypes. An armamentarium of imaging techniques including vascular ultrasound, echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, noninvasive computed tomography angiography, positron emission tomography, and nuclear imaging, with intrinsic strengths and limitations can be utilized to delineate incipient CVD for both clinical and research purposes. In this article, we review the various imaging modalities used for the evaluation, characterization, and quantification of early subclinical cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cardiovascular diseases; heart failure; phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
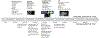






References
-
- Reddy KS. Cardiovascular Disease in Non-Western Countries. https://doi.org/101056/NEJMp048024. 2004;350(24):2438–2440. doi: 10.1056/NEJMP048024 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Newman WPI, Freedman DS, Voors AW, et al. Relation of Serum Lipoprotein Levels and Systolic Blood Pressure to Early Atherosclerosis. http://dx.doi.org/101056/NEJM198601163140302. 2009;314(3):138–144. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601163140302 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300025C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300027C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300026C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900041C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300028C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300029C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

