Genome-wide association study and functional characterization identifies candidate genes for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake
- PMID: 37291194
- PMCID: PMC7614755
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-023-01408-9
Genome-wide association study and functional characterization identifies candidate genes for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake
Abstract
Distinct tissue-specific mechanisms mediate insulin action in fasting and postprandial states. Previous genetic studies have largely focused on insulin resistance in the fasting state, where hepatic insulin action dominates. Here we studied genetic variants influencing insulin levels measured 2 h after a glucose challenge in >55,000 participants from three ancestry groups. We identified ten new loci (P < 5 × 10-8) not previously associated with postchallenge insulin resistance, eight of which were shown to share their genetic architecture with type 2 diabetes in colocalization analyses. We investigated candidate genes at a subset of associated loci in cultured cells and identified nine candidate genes newly implicated in the expression or trafficking of GLUT4, the key glucose transporter in postprandial glucose uptake in muscle and fat. By focusing on postprandial insulin resistance, we highlighted the mechanisms of action at type 2 diabetes loci that are not adequately captured by studies of fasting glycemic traits.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
I Barroso: IB and spouse declare stock ownership in GlaxoSmithkline, Incyte Ltd and Inivata Ltd. J.C. Florez: Consulting honoraria from Goldfinch Bio and AstraZeneca; speaker honoraria from Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca and Merck for research lectures over which I had full control on content. M.E. Kleber: Employed by SYNLAB Holding Deutschland GmbH. C. Lindgren: CL receives grants from Bayer Ag & Novo Nordisk and her Husband works for Vertex. W. März: reports grants and personal fees from Siemens Diagnostics, grants and personal fees from Aegerion Pharmaceuticals, grants and personal fees from AMGEN, grants and personal fees from Astrazeneca, grants and personal fees from Danone Research, grants and personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from Hoffmann LaRoche, personal fees from MSD, grants and personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Synageva, grants and personal fees from BASF, grants from Abbott Diagnostics, grants and personal fees from Numares, outside the submitted work. W. März is employed by Synlab Holding Deutschland GmbH. J.B. Meigs: Academic Associate for Quest Diagnostics. S. O'Rahilly: S.O. has undertaken remunerated consultancy work for Pfizer, AstraZeneca, GSK and ERX Pharmaceuticals.N. Parakakis: Nikolaos Perakakis reports consulting honoraria from Bayer Vital GmbH and speaker honoraria from Novo Nordisk. J. Sundström: Shareholder in Anagram kommunikation AB and Symptoms Europe AB, outside of the present study. D. Vistisen: DV has received research grants from Bayer A/S, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk A/S and Boehringer Ingelheim. DV holds shares in Novo Nordisk A/S. E. Wheeler: EW is now an employee of AstraZeneca. B. Zethelius: Björn Zethelius is employed at the Swedish Medical Products Agency, SE-751 03 Uppsala, Sweden. The views expressed in this paper are the personal views of the authors and not necessarily the views of the Swedish government agency. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

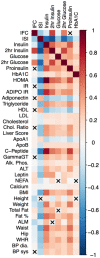

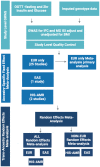



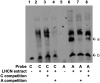




Comment in
-
Dynamic measures of insulin action identify genetic determinants of dysglycemia.Nat Genet. 2023 Jun;55(6):905-907. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01346-6. Nat Genet. 2023. PMID: 37291195 No abstract available.
References
-
- James DE, Stöckli J, Birnbaum MJ. The aetiology and molecular landscape of insulin resistance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:751–771. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92019D00031/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC UU 12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00014/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12012/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 HL129982/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S007091/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00006/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R00 AG066849/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK110550/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM135123/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

