Identification of a protective microglial state mediated by miR-155 and interferon-γ signaling in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37291336
- PMCID: PMC10619638
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01355-y
Identification of a protective microglial state mediated by miR-155 and interferon-γ signaling in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
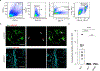
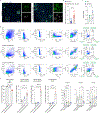
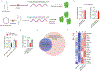
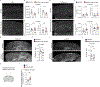
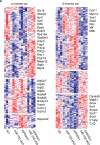
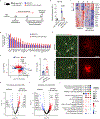
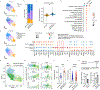
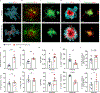
Microglia play a critical role in brain homeostasis and disease progression. In neurodegenerative conditions, microglia acquire the neurodegenerative phenotype (MGnD), whose function is poorly understood. MicroRNA-155 (miR-155), enriched in immune cells, critically regulates MGnD. However, its role in Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis remains unclear. Here, we report that microglial deletion of miR-155 induces a pre-MGnD activation state via interferon-γ (IFN-γ) signaling, and blocking IFN-γ signaling attenuates MGnD induction and microglial phagocytosis. Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis of microglia from an AD mouse model identifies Stat1 and Clec2d as pre-MGnD markers. This phenotypic transition enhances amyloid plaque compaction, reduces dystrophic neurites, attenuates plaque-associated synaptic degradation and improves cognition. Our study demonstrates a miR-155-mediated regulatory mechanism of MGnD and the beneficial role of IFN-γ-responsive pre-MGnD in restricting neurodegenerative pathology and preserving cognitive function in an AD mouse model, highlighting miR-155 and IFN-γ as potential therapeutic targets for AD.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
O.B. is an inventor of a patent for use of miR-155 inhibitors for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. O.B.: collaboration with GSK, Regulus Therapeutics; research funding from Sanofi, GSK, honoraria for lectures, consultancy: Camp4, Ono Pharma USA. T.I. consults Takeda. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG067763/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS101673/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 EY016335/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY027921/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R41 AG073059/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008541/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG072719/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054199/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS104609/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG051812/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM132668/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054199/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG066429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG075509/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS088137/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG076982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG080992/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG071106/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054672/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY030160/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG079859/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

