High-throughput RNA isoform sequencing using programmed cDNA concatenation
- PMID: 37291427
- PMCID: PMC12236355
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-023-01815-7
High-throughput RNA isoform sequencing using programmed cDNA concatenation
Abstract
Full-length RNA-sequencing methods using long-read technologies can capture complete transcript isoforms, but their throughput is limited. We introduce multiplexed arrays isoform sequencing (MAS-ISO-seq), a technique for programmably concatenating complementary DNAs (cDNAs) into molecules optimal for long-read sequencing, increasing the throughput >15-fold to nearly 40 million cDNA reads per run on the Sequel IIe sequencer. When applied to single-cell RNA sequencing of tumor-infiltrating T cells, MAS-ISO-seq demonstrated a 12- to 32-fold increase in the discovery of differentially spliced genes.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:
The authors declare the following competing interests:
The following provided funding that contributed to the subject matter of this manuscript: Broad Institute SPARC award, National Institutes of Health grants U19 AI082630, Adelson Medical Research Foundation, National Human Genome Research Institute grants RM1HG006193, support from the Center for Cell Circuits at the Broad Institute (HG006193), and Cancer Research Institute award 4071.
A.M.A., K.V.G., J.S., M.B., P.C.B., and N.H. are inventors on a licensed, pending international patent application, having Serial Number PCT/US2021/037226, filed by Broad Institute of MIT and Havard, Massachusetts General Hospital and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, directed to certain subject matter related to the MAS-seq method described in this manuscript.
Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Pacific Biosciences of California Inc. entered into a collaboration agreement relating to this research subsequent to the submission of this manuscript.
A.A.P. is a Venture Partner and Employee of GV. He has received funding from Verily, Microsoft, Illumina, Bayer, Pfizer, Biogen, Abbvie, Intel, and IBM.
M.S.F. receives funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
G.M.B. has served on SAB and on the steering committee for Nektar Therapeutics. She has SRAs with Olink proteomics and Palleon Pharmaceuticals. She served on SAB and as a speaker for Novartis.
N.H. holds equity in BioNTech and is a founder and equity holder of Danger Bio.
P.C.B. is a consultant to and/or holds equity in companies that develop or apply genomic or genome editing technologies: 10X Genomics, General Automation Lab Technologies/Isolation Bio, Celsius Therapeutics, Next Gen Diagnostics LLC, Cache DNA, Concerto Biosciences, Stately Bio, Ramona Optics, Bifrost Biosystems, and Amber Bio. P.C.B.’s group receives research funding from industry for unrelated work.
The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
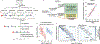
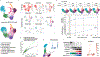
References
Methods references:
-
- Larsson AJM & Sandberg R stitcher.py. (2020). doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3765223. - DOI
-
- Pacific Biosciences, Inc. What is in the reads.bam? CCS Docs https://ccs.how/faq/reads-bam.html.
-
- Schreiber J Pomegranate: fast and flexible probabilistic modeling in python. arXiv [cs.AI] (2017).
-
- Durbin R, Eddy SR, Krogh A & Mitchison G Biological Sequence Analysis. Preprint at 10.1017/cbo9780511790492 (1998). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

