Evaluation of renal values during treatment for heartworm disease in 27 client-owned dogs
- PMID: 37291617
- PMCID: PMC10251593
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-023-05779-0
Evaluation of renal values during treatment for heartworm disease in 27 client-owned dogs
Abstract
Background: Canine heartworm disease (CHD) caused by Dirofilaria immitis remains a common preventable disease with increasing incidence in some parts of the USA. The treatment guidelines of the American Heartworm Society (AHS) currently recommend monthly macrocyclic lactone administration, 28 days of doxycycline given orally every 12 h and three injections of melarsomine dihydrochloride (1 injection on day 2 of treatment followed 30 days later by 2 injections 24 h apart). Minocycline has also been utilized when doxycycline is unavailable. The systemic effects of CHD, which particularly impact cardiac and renal function, have been described, with infected dogs often experiencing renal damage characterized by an increase in serum concentrations of renal biomarkers. Although the AHS treatment protocol for CHD has been shown to be safe and effective in most cases, the potential for complications remains. No study as of yet has evaluated changes in symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA), a sensitive marker of renal function, during treatment for CHD. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate renal function in dogs by measuring serum creatinine and SDMA concentrations during the adulticide treatment period.
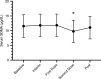
Methods: Serum creatinine and SDMA concentrations were measured in 27 client-owned dogs affected by CHD at the following time points: prior to starting doxycycline or minocycline therapy (baseline), during doxycycline or minocycline therapy (interim), at the time of the first dose of melarsomine (first dose), at the time of the second dose of melarsomine (second dose) and at the dog's follow-up visit after treatment, occurring between 1 and 6 months after completion of therapy (post-treatment). Concentrations of creatinine and SDMA were compared between time points using a mixed effects linear model.
Results: Mean SDMA concentrations following the second dose of melarsomine were significantly lower (-1.80 ug/dL, t-test, df = 99.067, t = -2.694, P-Value = 0.00829) than baseline concentrations. There were no other statistically significant differences in the concentration of either biomarker between the baseline and the other time points in CHD dogs undergoing treatment.
Conclusions: The results suggest that the current AHS protocol may not have a substantial impact on renal function.
Keywords: Canine; Dirofilaria immitis; Dirofilariasis; Kidney disease; Melarsomine; Symmetric dimethylarginine.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Heartworm control in Grenada, West Indies: Results of a field study using imidacloprid 10% + moxidectin 2.5% and doxycycline for naturally-acquired Dirofilaria immitis infections.Vet Parasitol. 2020 Aug;284:109194. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2020.109194. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Vet Parasitol. 2020. PMID: 32866837
-
Efficacy and side effects of doxycycline versus minocycline in the three-dose melarsomine canine adulticidal heartworm treatment protocol.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Dec 27;11(1):671. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3264-z. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 30587225 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of imidacloprid 10%/moxidectin 2.5% spot on (Advocate®, Advantage Multi®) and doxycycline for the treatment of natural Dirofilaria immitis infections in dogs.Vet Parasitol. 2019 Sep;273:11-16. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2019.07.011. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Vet Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31442887
-
Examination of the "susceptibility gap" in the treatment of canine heartworm infection.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Nov 9;10(Suppl 2):513. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2433-9. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 29143689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The safety-net story about macrocyclic lactone heartworm preventives: a review, an update, and recommendations.Vet Parasitol. 2005 Oct 24;133(2-3):197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.04.005. Epub 2005 Apr 26. Vet Parasitol. 2005. PMID: 16198822 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Successful management of acute kidney injury following interventional heartworm extraction in a dog with caval syndrome.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 31;12:1620928. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1620928. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40822652 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary NGAL as an Early Marker of Renal Dysfunction in Dogs with Heartworm Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 8;15(14):2003. doi: 10.3390/ani15142003. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Heartworm Society. Current canine guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, and management of heartworms (Dirofilaria immitis) infection in dogs. 2020. https://d3ft8sckhnqim2.cloudfront.net/images/pdf/AHS_Canine_Guidelines_1.... Accessed July 1 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

