Experience With Establishing a Robotic Donor Hepatectomy Program for Pediatric Liver Transplantation
- PMID: 37291714
- PMCID: PMC10664781
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004649
Experience With Establishing a Robotic Donor Hepatectomy Program for Pediatric Liver Transplantation
Abstract
Background: The benefits of minimal invasive donor hepatectomy, especially for left lateral sectionectomy (LLS) have been unequivocally demonstrated. Moreover, donors in pediatric liver transplantation (LT) are usually parents who need to recover quickly to take care of the child. There are inherent limitations to conventional laparoscopic surgery including surgeon's experience with advanced laparoscopic surgery and steep learning curve which limits the wide application of minimal invasive donor hepatectomy. We share our experience of establishing a program of robotic donor hepatectomy (RDH) and achieving proficiency in performing RDH for pediatric LT.
Methods: Data were prospectively collected of consecutive LLS RDH based on a structured learning algorithm. Donor and recipient outcomes were analyzed.
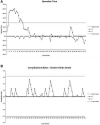
Results: Seventy-five consecutive cases of LLS RDH were performed. The median primary warm ischemia time was 6 min (interquartile range [IQR]: 5-7 min). No major complications (grade ≥IIIb Clavien-Dindo) were noted in the cohort. There were no emergency conversion to open surgery and neither were there postoperative explorations through a laparotomy. Seven grafts were hyper-reduced and 5 required venoplasty. Two recipients died because of severe sepsis and multiorgan failure. Major complications occurred in 15 children (20%), none of which were attributable to RDH. Median hospital stay of the donors and recipients was 5 d (IQR: 5-6) and 12 d (IQR: 10-18) respectively.
Conclusions: We share our experience of starting a RDH program for pediatric LT. We highlight the challenges and our learning algorithm to spur teams on the cusp of starting robotic transplant programs.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Comments on Experience With Establishing a Robotic Donor Hepatectomy Program for Pediatric Liver Transplantation.Transplantation. 2023 Dec 1;107(12):2458-2459. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004650. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Transplantation. 2023. PMID: 37291707 No abstract available.
-
Comment on Experience With Establishing a Robotic Donor Hepatectomy Program for Pediatric Liver Transplantation.Transplantation. 2024 Jul 1;108(7):e148. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004999. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Transplantation. 2024. PMID: 38917240 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cherqui D, Ciria R, Kwon CHD, et al. . Expert Consensus guidelines on minimally invasive donor hepatectomy for living donor liver transplantation from innovation to implementation: a joint initiative from the International Laparoscopic Liver Society (ILLS) and the Asian-Pacific Hepato-Pancreat. Ann Surg. 2021;273:96–108. - PubMed
-
- Brige P, Hery G, Chopinet S, et al. . Morbidity and mortality of hepatic right lobe living donors: systematic review and perspectives. J Gastrointest Liver Dis. 2018;27:169–178. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

