Irisin Ameliorates Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis by Regulating the Smad4/β-Catenin Pathway in Diabetic Mice
- PMID: 37292142
- PMCID: PMC10244207
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S407734
Irisin Ameliorates Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis by Regulating the Smad4/β-Catenin Pathway in Diabetic Mice
Abstract
Background: The primary pathophysiology of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is tubulointerstitial fibrosis (TIF), and an essential contributing element is excessive extracellular matrix deposition. Irisin is a polypeptide formed by splitting fibronectin type III domain containing 5 (FNDC5), which participates in a number of physiological and pathological processes.
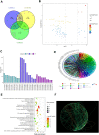
Methods: The purpose of this article is to examine irisin's function in DKD and analyze both its in vitro and in vivo effects. The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database was used to download GSE30122, GSE104954, and GSE99325. Analysis of renal tubule samples from nondiabetic and diabetic mice identified 94 differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFBR2), irisin, and TGF-β1 were utilized as DEGs to examine the impact of irisin on TIF in diabetic kidney tissue, according to the datasets retrieved from the GEO database and Nephroseq database. Additionally, the therapeutic impact of irisin was also examined using Western blot, RT-qPCR, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and kits for detecting mouse biochemical indices.
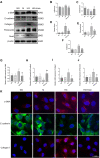
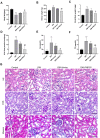
Results: In vitro, the findings demonstrated that irisin not only down-regulated the expression of Smad4 and β-catenin but also reduced the expression of proteins linked to fibrosis, the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and mitochondrial dysfunction in HK-2 cells maintained in high glucose (HG) environment. In vivo, overexpressed FNDC5 plasmid was injected into diabetic mice to enhance its expression. Our studies found that overexpressed FNDC5 plasmid not only reversed the biochemical parameters and renal morphological characteristics of diabetic mice but also alleviated EMT and TIF by inhibiting Smad4/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Conclusion: The above experimental results revealed that irisin could reduce TIF in diabetic mice via regulating the Smad4/β-catenin pathway.
Keywords: Smad4; diabetic kidney disease; irisin; tubulointerstitial fibrosis; β-catenin.
© 2023 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

