The role of nanotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by targeting tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 37292204
- PMCID: PMC10244756
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1189323
The role of nanotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by targeting tumor microenvironment
Abstract
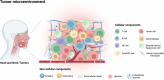
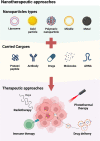
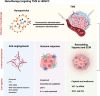
Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) refers to a group of highly malignant and pathogenically complex tumors. Traditional treatment methods include surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. However, with advancements in genetics, molecular medicine, and nanotherapy, more effective and safer treatments have been developed. Nanotherapy, in particular, has the potential to be an alternative therapeutic option for HNSCC patients, given its advantageous targeting capabilities, low toxicity and modifiability. Recent research has highlighted the important role of the tumor microenvironment (TME) in the development of HNSCC. The TME is composed of various cellular components, such as fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells, and immune cells, as well as non-cellular agents such as cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, extracellular matrix (ECM), and extracellular vesicles (EVs). These components greatly influence the prognosis and therapeutic efficacy of HNSCC, making the TME a potential target for treatment using nanotherapy. By regulating angiogenesis, immune response, tumor metastasis and other factors, nanotherapy can potentially alleviate HNSCC symptoms. This review aims to summarize and discuss the application of nanotherapy that targets HNSCC's TME. We highlight the therapeutic value of nanotherapy for HNSCC patients.
Keywords: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; immune microenvironment; immune response; nanotherapy; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Dong and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioinformatic analysis identifies HPV-related tumor microenvironment remodeling prognostic biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 8;12:1007950. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1007950. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36425786 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Head and Neck Tumor Microenvironment-Based Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1296:11-31. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-59038-3_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 34185284
-
Tumor immune microenvironment in head and neck cancers.Mol Carcinog. 2020 Jul;59(7):766-774. doi: 10.1002/mc.23162. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Mol Carcinog. 2020. PMID: 32017286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive investigation into the influence of glycosylation on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and development of a prognostic model for risk assessment and anticipating immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 18;15:1364082. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1364082. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38562924 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine-Cytokine Networks in the Head and Neck Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 27;22(9):4584. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094584. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925575 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precision USPIO-PEG-SLex Nanotheranostic Agent Targeted Photothermal Therapy for Enhanced Anti-PD-L1 Immunotherapy to Treat Immunotherapy Resistance.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Feb 7;19:1249-1272. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S445879. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38348177 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Current Insights and Treatment Advances.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 24;17(1):4. doi: 10.3390/cancers17010004. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39796633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology in the perioperative treatment of head and neck cancer: application and outlook.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 27;13:1566522. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1566522. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40213641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current nano drug delivery systems for targeting head and neck squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment: a narrative review.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Apr 8;52(1):369. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10462-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40195238 Review.
-
Role of Microenvironmental Components in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Pers Med. 2023 Nov 17;13(11):1616. doi: 10.3390/jpm13111616. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38003931 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

