Arctigenin hinders the invasion and metastasis of cervical cancer cells via the FAK/paxillin pathway
- PMID: 37292259
- PMCID: PMC10245248
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16683
Arctigenin hinders the invasion and metastasis of cervical cancer cells via the FAK/paxillin pathway
Abstract
Context: Cervical cancer is the most common gynecological pernicious tumor with high morbidity and mortality worldwide, especially in developing countries. Arctigenin (ARG), a nature-derived component, has exhibited anti-tumor activity in various tumors.
Objective: To explore the effect of ARG on cervical cancer.
Materials and methods: The effect and mechanism of ARG on cervical cancer cells were explored by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), flow cytometry, transwell and Western blot assays. Additionally, in vivo experiment was conducted in xenografted mice by immunohistochemistry (IHC), terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) nick end labeling (TUNEL) and Western blot assays.
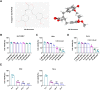
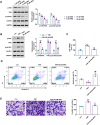
Results: ARG treatment induced both concentration-dependent and time-dependent reductions in the cell viability of SiHa and HeLa cells with a IC50 value of 9.34 μM and 14.45 μM, respectively. ARG increased the apoptosis rate and the protein levels of cleaved-caspase 3 and E-cadherin, but decreased the invaded cell numbers and the protein levels of Vimentin and N-cadherin in vitro. Mechanically, ARG inhibited the expression of focal adhesion kinase (FAK)/paxillin pathway, which was confirmed by the overexpression of FAK in SiHa cells. The inhibitory role of overexpression of FAK in proliferation and invasion, as well as its promoted role in apoptosis were reversed with ARG treatment. Meanwhile, ARG suppressed growth and metastasis, and enhanced apoptosis in vivo. Consistently, ARG administration reduced the relative protein level of p-FAK/FAK and p-paxillin/paxillin in tumor tissues of xenografted mice.
Conclusion: ARG inhibited proliferation, invasion and metastasis, but enhanced apoptosis of cervical cancer via the FAK/paxillin axis.
Keywords: Arctigenin; Cervical cancer; FAK/Paxillin; Invasion; Metastasis.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genistein inhibits migration and invasion of cervical cancer HeLa cells by regulating FAK-paxillin and MAPK signaling pathways.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May;59(3):403-408. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2020.03.012. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32416888
-
Genistein inhibits the growth and regulates the migration and invasion abilities of melanoma cells via the FAK/paxillin and MAPK pathways.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 28;8(13):21674-21691. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15535. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423510 Free PMC article.
-
Bit1 knockdown contributes to growth suppression as well as the decreases of migration and invasion abilities in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via suppressing FAK-paxillin pathway.Mol Cancer. 2016 Mar 8;15:23. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0507-5. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26956728 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase enhances gastric cancer progression via the FAK/Paxillin pathway.Mol Cancer. 2014 May 4;13:100. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-100. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24885567 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of L1 cell adhesion molecule interacting with protein tyrosine kinase 2 to regulate the focal adhesion kinase-growth factor receptor-bound protein 2-son of sevenless-rat sarcoma pathway in the identification and treatment of type I high-risk endometrial cancer.Cytojournal. 2024 Sep 30;21:34. doi: 10.25259/Cytojournal_50_2024. eCollection 2024. Cytojournal. 2024. PMID: 39563667 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
LIMK1 promotes the development of cervical cancer by up-regulating the ROS/Src-FAK/cofilin signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jul 5;16(13):11090-11102. doi: 10.18632/aging.206007. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38975937 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MALAT1 facilitates BM-MSCs differentiation into endothelial cells and ameliorates erectile dysfunction via the miR-206/CDC42/PAK1/paxillin signalling axis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Jun 25;22(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01240-8. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38918809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gupta S., Maheshwari A., Parab P., Mahantshetty U., Hawaldar R., Sastri Chopra S., Kerkar R., Engineer R., Tongaonkar H., Ghosh J., et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by radical surgery versus concomitant chemotherapy and radiotherapy in patients with stage IB2, IIA, or IIB squamous cervical cancer: a randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36(16):1548–1555. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.75.9985. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Volarevic V., Djokovic B., Jankovic M.G., Harrell C.R., Fellabaum C., Djonov V., Arsenijevic N. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: a balance on the knife edge between renoprotection and tumor toxicity. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019;26(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0518-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

