Parameters optimization of Fe3O4 NPs synthesis by Tamarindus indica leaf extract possessing both peroxidase as well as excellent dye removal activity
- PMID: 37292316
- PMCID: PMC10245268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16699
Parameters optimization of Fe3O4 NPs synthesis by Tamarindus indica leaf extract possessing both peroxidase as well as excellent dye removal activity
Abstract
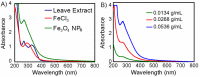
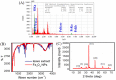
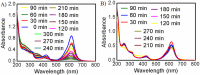
This study reports optimized conditions for the green synthesis of iron (II,III) oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) from Tamarindus indica (T. indica) leaf extract. The synthetic parameters like concentration of leaf extract, solvent system, buffer, electrolyte, pH, and time were optimized for Fe3O4 NPs synthesis. Fe3O4 NPs were obtained from the synthesis protocol by measuring size (80 3 nm approx.), characteristics color changes, and an absorption peak between 270 nm and 280 nm using a UV-visible spectrophotometer, scanning electron microscope (SEM), and an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS) study. Peroxidase activity was tested with 3,3,5,5-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) oxidation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide and dye removal activity was tested with malachite green (MG). The results indicated that the successful synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of T. indica is a practical alternative for biomedical applications due to its potent peroxidase activity and high dye removal capacity (about 93% with UV light and 55% with room light).
Keywords: Dye removal activity; Fe3O4 nanoparticle; Green synthesis; Peroxidase activity; Tamarindus indica leaf Extract.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Braunschweig J., Bosch J., Meckenstock R.U. Iron oxide nanoparticles in geomicrobiology: from biogeochemistry to bioremediation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013;30:793–802. - PubMed
-
- Gupta A.K., Gupta M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2005;26:3995–4021. - PubMed
-
- Li X.-Q., Elliott D.W., Zhang W.-X. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for abatement of environmental pollutants: materials and engineering aspects. Crit. Rev. Solid State. 2006;31:111–122.
-
- López-Serrano A., Olivas R.M., Landaluze J.S., Cámara C. Nanoparticles: a global vision. Characterization, separation, and quantification methods. Potential environmental and health impact. Anal. Methods. 2014;6:38–56.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

