Fine-grained detection on the public's multi-dimensional communication preferences in emergency events
- PMID: 37292357
- PMCID: PMC10245013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16312
Fine-grained detection on the public's multi-dimensional communication preferences in emergency events
Abstract
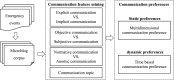
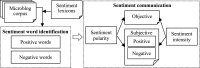
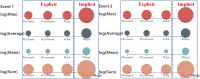
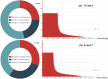
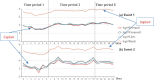
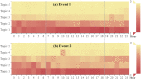
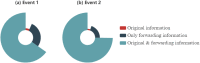
With the rapid development of Internet technologies, the public can participate in the information communication of emergency events more conveniently and quickly. Once an emergency occurs, the public will immediately express and disseminate massive information about the causes, processes and results of the emergency. In the process of information communication, the public often adopts diversified communication modes, and then shows differential communication preferences. The detection of the public's communication preferences can more accurately understand the information demands of the public in events, and then contribute to the rational allocation of resources and improve the processing efficiency. Therefore, this paper conducted finer-grained mining on the public's online expressions in multiple events, so as to detect the public's communication preferences. Specifically, we collected the public's expressions related to emergency events from the social media and then we analyzed the expressions from multiple dimensions to obtain the corresponding communication features. Finally, based on the comparative analysis of diversified communication features, static and dynamic communication preferences were obtained. The experimental results indicate that the public's communication preferences do exist, which is universal and consistent. Meanwhile, constructing a better social environment and improving people's livelihood are the fundamental strategies to guide public opinion.
Keywords: Anomie detection; Emergency event; Information communication preference; Public opinion; Sentiment analysis; Topic extraction.
© 2023 The Author.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors have no interests to declare.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Public Attention and Sentiment toward Intimate Partner Violence Based on Weibo in China: A Text Mining Approach.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;10(2):198. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10020198. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35206813 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of the Public's Aversion to Patients Infected with COVID-19 in China: The Mediating Role of Negative Physiology.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Sep 20;10(10):1813. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10101813. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292260 Free PMC article.
-
Should Waste Separation Be Mandatory? A Study on Public's Response to the Policies in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jun 24;17(12):4539. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17124539. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32599737 Free PMC article.
-
The Public's Preferences for Psychological Interventions During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Discrete Choice Experiment.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Apr 27;13:805512. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.805512. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35573350 Free PMC article.
-
The history of anatomical engagement.Anat Sci Educ. 2025 Feb 5. doi: 10.1002/ase.70000. Online ahead of print. Anat Sci Educ. 2025. PMID: 39910807 Review.
References
-
- Nayar P.K. Shaping the network society: the new role of civil society in cyberspace. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006;57(5):724–725.
-
- Kim K.S., Sin S., Yoo-Lee E.Y. Use and evaluation of information from social media: a longitudinal cohort study. Libr. Inf. Sci. Res. 2021;43(3)
-
- Cortez B., Carrera B., Kim Y.J., Jung J.Y. An architecture for emergency event prediction using LSTM recurrent neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018;97:315–324.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

