A Case of Non-purpuric Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia Secondary to ABO Incompatibility
- PMID: 37292561
- PMCID: PMC10247154
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.38728
A Case of Non-purpuric Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia Secondary to ABO Incompatibility
Abstract
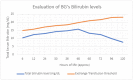
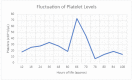
Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia (NAIT) is a condition in which maternal IgG antibodies are directed against fetal platelets and cross the placenta, destroying fetal thrombocytes. It is typically caused by maternal alloimmunization to human leukocyte antigens (HLA). ABO incompatibility, on the other hand, is a rare cause of NAIT due to the variable expression of ABO antigens on platelets. Here, we present the case of a first-time mother (O+) who delivered a 37-week 0-day gestation newborn (B+) that was anemic and jaundiced with critically high total bilirubin levels. This required the initiation of phototherapy and intravenous immunoglobulins. Despite treatment, jaundice was slow to improve. Given infectious concerns, a complete white blood cell count was ordered. Incidentally, it revealed severe thrombocytopenia. Platelet transfusions were administered, although only minimal improvement was observed. This warranted maternal testing for antibodies to HLA-Ia/IIa, HLA-IIb/IIIa, and HLA-Ib/IX antigens given suspected NAIT. Results returned negative. Due to the severity of the condition, patient care was continued at a tertiary facility. When screening for NAIT, special consideration should be given to type O mothers with ABO incompatibility to their fetus - they can uniquely make IgG against A or B antigens, which, unlike IgM and IgA, can cross the placenta and cause potential sequelae harming the newborn. Early recognition and timely management of NAIT are important to prevent certain complications, such as fatal intracranial hemorrhage and developmental delay.
Keywords: abo compatibility; fitzpatrick type v; igg antibody; neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia; nonpurpuric.
Copyright © 2023, Arthurs et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ABO incompatibility: A cause for neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia.Asian J Transfus Sci. 2023 Jan-Jun;17(1):133-135. doi: 10.4103/ajts.ajts_194_20. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2023. PMID: 37188011 Free PMC article.
-
[Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Sep;55(9):2310-4. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9301295 Review. Japanese.
-
What's happening? The expanding role of apheresis platelet support in neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia: current status and future trends.Transfus Apher Sci. 2005 Oct;33(2):191-7. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2005.06.001. Transfus Apher Sci. 2005. PMID: 16140039
-
Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia associated with maternal anti-HLA antibody: a case report.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1998 May-Jun;20(3):252-6. doi: 10.1097/00043426-199805000-00012. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1998. PMID: 9628438
-
Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia: A Concise Review.Adv Neonatal Care. 2021 Apr 1;21(2):115-121. doi: 10.1097/ANC.0000000000000775. Adv Neonatal Care. 2021. PMID: 32657948 Review.
References
-
- Fernandes CJ. Neonatal immune-mediated thrombocytopenia. [ Jan; 2023 ];Fernandes CJ. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/neonatal-immune-mediated-thrombocytope... 2021 13:2023.
-
- Paidas MM. Fetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia: parental evaluation and pregnancy management. [ Feb; 2023 ];Paidas MM. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/fetal-and-neonatal-alloimmune-thromboc... 2022 5:2023.
-
- Blood group A and B antigens are strongly expressed on platelets of some individuals. Curtis BR, Edwards JT, Hessner MJ, Klein JP, Aster RH. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10942408/ Blood. 2000;96:1574–1581. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous