This is a preprint.
Insights into human health from phenome- and genome-wide analyses of UK Biobank retinal optical coherence tomography phenotypes
- PMID: 37292770
- PMCID: PMC10246137
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.05.16.23290063
Insights into human health from phenome- and genome-wide analyses of UK Biobank retinal optical coherence tomography phenotypes
Abstract
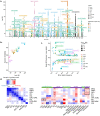
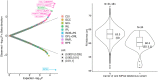
The human retina is a complex multi-layered tissue which offers a unique window into systemic health and disease. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is widely used in eye care and allows the non-invasive, rapid capture of retinal measurements in exquisite detail. We conducted genome- and phenome-wide analyses of retinal layer thicknesses using macular OCT images from 44,823 UK Biobank participants. We performed phenome-wide association analyses, associating retinal thicknesses with 1,866 incident ICD-based conditions (median 10-year follow-up) and 88 quantitative traits and blood biomarkers. We performed genome-wide association analyses, identifying inherited genetic markers which influence the retina, and replicated our associations among 6,313 individuals from the LIFE-Adult Study. And lastly, we performed comparative association of phenome- and genome- wide associations to identify putative causal links between systemic conditions, retinal layer thicknesses, and ocular disease. Independent associations with incident mortality were detected for photoreceptor thinning and ganglion cell complex thinning. Significant phenotypic associations were detected between retinal layer thinning and ocular, neuropsychiatric, cardiometabolic and pulmonary conditions. Genome-wide association of retinal layer thicknesses yielded 259 loci. Consistency between epidemiologic and genetic associations suggested putative causal links between thinning of the retinal nerve fiber layer with glaucoma, photoreceptor segment with AMD, as well as poor cardiometabolic and pulmonary function with PS thinning, among other findings. In conclusion, retinal layer thinning predicts risk of future ocular and systemic disease. Furthermore, systemic cardio-metabolic-pulmonary conditions promote retinal thinning. Retinal imaging biomarkers, integrated into electronic health records, may inform risk prediction and potential therapeutic strategies.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phenome- and genome-wide analyses of retinal optical coherence tomography images identify links between ocular and systemic health.Sci Transl Med. 2024 Jan 24;16(731):eadg4517. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adg4517. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Sci Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38266105
-
Photoreceptor Layer Thinning Is an Early Biomarker for Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Epidemiologic and Genetic Evidence from UK Biobank OCT Data.Ophthalmology. 2022 Jun;129(6):694-707. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2022.02.001. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Ophthalmology. 2022. PMID: 35149155 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal Layer Thicknesses in Early Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Results From the German AugUR Study.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Apr 1;60(5):1581-1594. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-25332. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30995315 Free PMC article.
-
Optical coherence tomography in mild cognitive impairment - Systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Sep;196:106036. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106036. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32623211
-
Advancements in Machine Learning for Precision Diagnostics and Surgical Interventions in Interconnected Musculoskeletal and Visual Systems.J Clin Med. 2025 May 23;14(11):3669. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113669. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507433 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Solberg Y., Rosner M., Belkin M., The association between cigarette smoking and ocular diseases. [Review] [162 refs]. Surv Ophthalmol 42 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
