This is a preprint.
Development of Cas13a-based Assays for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Detection and Gyrase A Determination
- PMID: 37293004
- PMCID: PMC10246164
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.05.21.23290304
Development of Cas13a-based Assays for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Detection and Gyrase A Determination
Update in
-
Development of Cas13a-based assays for Neisseria gonorrhoeae detection and gyrase A determination.mSphere. 2023 Oct 24;8(5):e0041623. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00416-23. Epub 2023 Sep 21. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 37732792 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Neisseria gonorrhoeae is one of the most common bacterial sexually transmitted infections. The emergence of antimicrobial-resistant N. gonorrhoeae is an urgent public health threat. Currently, diagnosis of N. gonorrhoeae infection requires expensive laboratory infrastructure, while antimicrobial susceptibility determination requires bacterial culture, both of which are infeasible in low-resource areas where prevalence is highest. Recent advances in molecular diagnostics, such as Specific High-sensitivity Enzymatic Reporter unLOCKing (SHERLOCK) using CRISPR-Cas13a and isothermal amplification, have the potential to provide low-cost detection of pathogen and antimicrobial resistance.
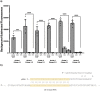
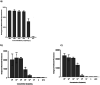
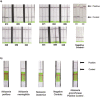
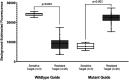
Methods and results: We designed and optimized RNA guides and primer-sets for SHERLOCK assays capable of detecting N. gonorrhoeae via the por A gene and of predicting ciprofloxacin susceptibility via a single mutation in the gyrase A ( gyr A) gene. We evaluated their performance using both synthetic DNA and purified N. gonorrhoeae isolates. For por A, we created both a fluorescence-based assay and lateral flow assay using a biotinylated FAM reporter. Both methods demonstrated sensitive detection of 14 N. gonorrhoeae isolates and no cross-reactivity with 3 non-gonococcal Neisseria isolates. For gyr A, we created a fluorescence-based assay that correctly distinguished between 20 purified N. gonorrhoeae isolates with phenotypic ciprofloxacin resistance and 3 with phenotypic susceptibility. We confirmed the gyr A genotype predictions from the fluorescence-based assay with DNA sequencing, which showed 100% concordance for the isolates studied.
Conclusion: We report the development of Cas13a-based SHERLOCK assays that detect N. gonorrhoeae and differentiate ciprofloxacin-resistant isolates from ciprofloxacin-susceptible isolates.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of Cas13a-based assays for Neisseria gonorrhoeae detection and gyrase A determination.mSphere. 2023 Oct 24;8(5):e0041623. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00416-23. Epub 2023 Sep 21. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 37732792 Free PMC article.
-
Development and application of Cas13a-based diagnostic assay for Neisseria gonorrhoeae detection and azithromycin resistance identification.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022 Feb 23;77(3):656-664. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab447. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022. PMID: 34894246
-
Preliminary clinical performance of a Cas13a-based lateral flow assay for detecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae in urine specimens.mSphere. 2025 Jan 28;10(1):e0067724. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00677-24. Epub 2024 Dec 17. mSphere. 2025. PMID: 39688405 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial susceptibilities of strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Bangkok, Thailand: 1994-1995.Sex Transm Dis. 1997 Mar;24(3):142-8. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199703000-00004. Sex Transm Dis. 1997. PMID: 9132980
-
Expanding U.S. Laboratory Capacity for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Whole-Genome Sequencing through the CDC's Antibiotic Resistance Laboratory Network.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Mar 25;58(4):e01461-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01461-19. Print 2020 Mar 25. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32024723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vaezzadeh K, Sepidarkish M, Mollalo A, As'adi N, Rouholamin S, Rezaeinejad M, et al. Global prevalence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection in pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2023;29(1):22–31. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
