Erdafitinib treatment in metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a real-world analysis
- PMID: 37293597
- PMCID: PMC10244774
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1151701
Erdafitinib treatment in metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a real-world analysis
Abstract
Background: Erdafitinib, a fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor is a standard post chemotherapy advanced treatment line for metastatic urothelial carcinoma harboring FGFR2/3 genomic alterations. It was approved based on a phase 2 clinical trial, revealing a 40% response rate, and 13.8 months overall survival. These FGFR genomic alterations are uncommon. Thus, real-world data on erdafitinb use is scant. We herein describe erdafitinib treatment outcome in a real world patient cohort.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the data of patients treated with erdafitinib from 9 Israeli medical centers.
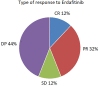
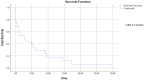
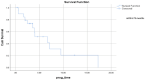
Results: Twenty-five patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma (median age 73, 64% male, 80% with visceral metastases) were treated with erdafitinib between January 2020 to October 2022. A clinical benefit (complete response 12%, partial response 32%, stable disease 12%) was seen in 56%. Median progression-free survival was 2.7 months, and median overall survival 6.73 months. Treatment related toxicity ≥ grade 3 occurred in 52%, and 32% discontinued therapy due to adverse events.
Conclusions: Erdafitinib therapy is associated with a clinical benefit in the real world setting, and associated with similar toxicity as reported in prospective clinical trials.
Keywords: erdafitinib; fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor; metastatic urothelial carcinoma; real-world analysis; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Rouvinov, Levanon, Peer, Sarfaty, Sarid, Neiman, Grikshtas, Rosenbaum, Kushnir, Talmor, Friger, Zarbiv, Gez, Dresler, Shalata, Meirovitz, Shrem, Yakobson, Mermershtain and Keizman.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Monteiro FSM, Silva AGE, Gomes AJP de S, Dutra C, Ferreira NO, Mariano RC, et al. . Erdafitinib treatment in Brazilian patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma (mUC): real–world evidence from an expanded access program. Ther Adv Med Oncol (2021) 13:175883592110154. doi: 10.1177/17588359211015499 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siefker–Radtke AO, Necchi A, Park SH, García–Donas J, Huddart RA, Burgess EF, et al. . Efficacy and safety of erdafitinib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: long–term follow–up of a phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol (2022) 23(2):248–58. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00660-4 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous