Natural flavonoids disrupt bacterial iron homeostasis to potentiate colistin efficacy
- PMID: 37294761
- PMCID: PMC10256158
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg4205
Natural flavonoids disrupt bacterial iron homeostasis to potentiate colistin efficacy
Abstract
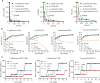
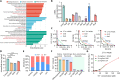
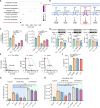
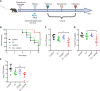
In the face of the alarming rise in global antimicrobial resistance, only a handful of novel antibiotics have been developed in recent decades, necessitating innovations in therapeutic strategies to fill the void of antibiotic discovery. Here, we established a screening platform mimicking the host milieu to select antibiotic adjuvants and found three catechol-type flavonoids-7,8-dihydroxyflavone, myricetin, and luteolin-prominently potentiating the efficacy of colistin. Further mechanistic analysis demonstrated that these flavonoids are able to disrupt bacterial iron homeostasis through converting ferric iron to ferrous form. The excessive intracellular ferrous iron modulated the membrane charge of bacteria via interfering the two-component system pmrA/pmrB, thereby promoting the colistin binding and subsequent membrane damage. The potentiation of these flavonoids was further confirmed in an in vivo infection model. Collectively, the current study provided three flavonoids as colistin adjuvant to replenish our arsenals for combating bacterial infections and shed the light on the bacterial iron signaling as a promising target for antibacterial therapies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rutin Synergizes with Colistin to Eradicate Salmonellosis in Mice by Enhancing the Efficacy and Reducing the Toxicity.J Agric Food Chem. 2025 Jan 8;73(1):438-449. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c06751. Epub 2024 Dec 19. J Agric Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39699161
-
Mechanism of Action of Isopropoxy Benzene Guanidine against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0346922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03469-22. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36475769 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Novel Amino Acid Alterations in PmrA or PmrB to Colistin Resistance in mcr-Negative Escherichia coli Clinical Isolates, Including Major Multidrug-Resistant Lineages O25b:H4-ST131-H30Rx and Non-x.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Aug 27;62(9):e00864-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00864-18. Print 2018 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29914952 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of polymyxin resistance and detection of mcr genes.Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2019 Feb;163(1):28-38. doi: 10.5507/bp.2018.070. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2019. PMID: 30439931 Review.
-
Rescuing humanity by antimicrobial peptides against colistin-resistant bacteria.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;106(11):3879-3893. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11940-z. Epub 2022 May 23. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35604438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of aloe emodin, emodin, and rhein from Aloe with EDTA sensitizes the resistant Acinetobacter baumannii to polymyxins.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 13;14:1467607. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1467607. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39346899 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Outer Membrane Vesicles with Genetically Engineering for Treatment of Implant-Associated Infections and Relapse Prevention Through Host Immunomodulation.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(14):e2415379. doi: 10.1002/advs.202415379. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39950746 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Flavonoid Research: Sources, Biological Activities, and Developmental Prospectives.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Mar 26;46(4):2884-2925. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040181. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Combination of Antibiotic and Non-Antibiotic Compounds Improves Antibiotic Efficacy against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15493. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015493. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Valnemulin restores colistin sensitivity against multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 12;7(1):1122. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06805-2. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39261709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- E. D. Brown, G. D. Wright, Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature 529, 336–343 (2016). - PubMed
-
- B. M. Kuehn, Alarming antimicrobial resistance trends emerge globally. JAMA 324, 223 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Y.-Y. Liu, Y. Wang, T. R. Walsh, L.-X. Yi, R. Zhang, J. Spencer, Y. Doi, G. Tian, B. Dong, X. Huang, L.-F. Yu, D. Gu, H. Ren, X. Chen, L. Lv, D. He, H. Zhou, Z. Liang, J.-H. Liu, J. Shen, Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 16, 161–168 (2016). - PubMed
-
- J. Sun, C. Chen, C.-Y. Cui, Y. Zhang, X. Liu, Z.-H. Cui, X.-Y. Ma, Y. Feng, L.-X. Fang, X.-L. Lian, R.-M. Zhang, Y.-Z. Tang, K.-X. Zhang, H.-M. Liu, Z.-H. Zhuang, S.-D. Zhou, J.-N. Lv, H. Du, B. Huang, F.-Y. Yu, B. Mathema, B. N. Kreiswirth, X.-P. Liao, L. Chen, Y.-H. Liu, Plasmid-encoded tet(X) genes that confer high-level tigecycline resistance in Escherichia coli. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 1457–1464 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

