Temperature-dependent RNA editing in octopus extensively recodes the neural proteome
- PMID: 37295402
- PMCID: PMC10445230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.05.004
Temperature-dependent RNA editing in octopus extensively recodes the neural proteome
Abstract
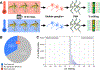
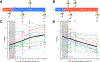
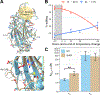
In poikilotherms, temperature changes challenge the integration of physiological function. Within the complex nervous systems of the behaviorally sophisticated coleoid cephalopods, these problems are substantial. RNA editing by adenosine deamination is a well-positioned mechanism for environmental acclimation. We report that the neural proteome of Octopus bimaculoides undergoes massive reconfigurations via RNA editing following a temperature challenge. Over 13,000 codons are affected, and many alter proteins that are vital for neural processes. For two highly temperature-sensitive examples, recoding tunes protein function. For synaptotagmin, a key component of Ca2+-dependent neurotransmitter release, crystal structures and supporting experiments show that editing alters Ca2+ binding. For kinesin-1, a motor protein driving axonal transport, editing regulates transport velocity down microtubules. Seasonal sampling of wild-caught specimens indicates that temperature-dependent editing occurs in the field as well. These data show that A-to-I editing tunes neurophysiological function in response to temperature in octopus and most likely other coleoids.
Keywords: ADAR; RNA editing; RNA modifications; acclimation; cephalopod; epitranscriptome; kinesin; neural plasticity; synaptotagmin; temperature.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Chilling with cephalopods: Temperature-responsive RNA editing in octopus and squid.Cell. 2023 Jun 8;186(12):2518-2520. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.05.021. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37295397
-
Temperature-induced RNA recoding in octopus.Nat Genet. 2023 Jul;55(7):1082. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01456-1. Nat Genet. 2023. PMID: 37438536 No abstract available.
References
-
- Carpenter DO. (1981). Ionic and metabolic bases of neuronal thermosensitivity. Fed. Proc. 40, 2808–2813. - PubMed
-
- Montgomery JC, and MacDonald JA. (1990). Effects of temperature on nervous system: implications for behavioral performance. Am. J. Physiol. - Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 28, R191–R196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

