The YEATS domain epigenetic reader proteins ENL and AF9 and their therapeutic value in leukemia
- PMID: 37295550
- PMCID: PMC10527611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2023.06.001
The YEATS domain epigenetic reader proteins ENL and AF9 and their therapeutic value in leukemia
Abstract
Recent studies have uncovered similarities and differences between 2 highly homologous epigenetic reading proteins, namely, ENL (MLLT1) and AF9 (MLLT3) with therapeutic implications. The importance of these proteins has traditionally been exemplified by their involvement in chromosomal translocations with the mixed-lineage leukemia gene (MLL; aka KMT2a). MLL rearrangements occur in a subset of acute leukemias and generate potent oncogenic MLL-fusion proteins that impact epigenetic and transcriptional regulation. Leukemic patients with MLL rearrangements display intermediate-to-poor prognoses, necessitating further mechanistic research. Several protein complexes involved in regulating RNA polymerase II transcription and the epigenetic landscape are hijacked in MLL-r leukemia, which include ENL and AF9. Recent biochemical studies have defined a highly homologous YEATS domain in ENL and AF9 that binds acylated histones, which aids in the localization and retention of these proteins to transcriptional targets. In addition, detailed characterization of the homologous ANC-1 homology domain (AHD) on ENL and AF9 revealed differential association with transcriptional activating and repressing complexes. Importantly, CRISPR knockout screens have demonstrated a unique role for wild-type ENL in leukemic stem cell function, whereas AF9 appears important for normal hematopoietic stem cells. In this perspective, we examine the ENL and AF9 proteins with attention to recent work characterizing the epigenetic reading YEATS domains and AHD on both wild-type proteins and when fused to MLL. We summarized the drug development efforts and their therapeutic potential and assess ongoing research that has refined our understanding of how these proteins function, which continues to reveal new therapeutic avenues.
Copyright © 2023 ISEH -- Society for Hematology and Stem Cells. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosure The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to declare in relation to this work.
Figures
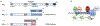
References
-
- Ziemin-van der Poel S, McCabe NR, Gill HJ, Espinosa R, Patel Y, Harden A, et al. Identification of a gene, MLL, that spans the breakpoint in 11q23 translocations associated with human leukemias. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1991;88:10735–9. 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doty RT, Vanasse GJ, Disteche CM, Willerford DM. The leukemia-associated gene Mllt1/ENL: characterization of a murine homolog and demonstration of an essential role in embryonic development. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2002;28:407–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

