Xylosyltransferase I mediates the synthesis of proteoglycans with long glycosaminoglycan chains and controls chondrocyte hypertrophy and collagen fibers organization of in the growth plate
- PMID: 37296099
- PMCID: PMC10256685
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-05875-0
Xylosyltransferase I mediates the synthesis of proteoglycans with long glycosaminoglycan chains and controls chondrocyte hypertrophy and collagen fibers organization of in the growth plate
Abstract
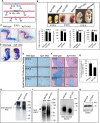
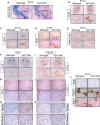
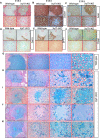
Genetic mutations in the Xylt1 gene are associated with Desbuquois dysplasia type II syndrome characterized by sever prenatal and postnatal short stature. However, the specific role of XylT-I in the growth plate is not completely understood. Here, we show that XylT-I is expressed and critical for the synthesis of proteoglycans in resting and proliferative but not in hypertrophic chondrocytes in the growth plate. We found that loss of XylT-I induces hypertrophic phenotype-like of chondrocytes associated with reduced interterritorial matrix. Mechanistically, deletion of XylT-I impairs the synthesis of long glycosaminoglycan chains leading to the formation of proteoglycans with shorter glycosaminoglycan chains. Histological and Second Harmonic Generation microscopy analysis revealed that deletion of XylT-I accelerated chondrocyte maturation and prevents chondrocytes columnar organization and arrangement in parallel of collagen fibers in the growth plate, suggesting that XylT-I controls chondrocyte maturation and matrix organization. Intriguingly, loss of XylT-I induced at embryonic stage E18.5 the migration of progenitor cells from the perichondrium next to the groove of Ranvier into the central part of epiphysis of E18.5 embryos. These cells characterized by higher expression of glycosaminoglycans exhibit circular organization then undergo hypertrophy and death creating a circular structure at the secondary ossification center location. Our study revealed an uncovered role of XylT-I in the synthesis of proteoglycans and provides evidence that the structure of glycosaminoglycan chains of proteoglycans controls chondrocyte maturation and matrix organization.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
TMEM165 a new player in proteoglycan synthesis: loss of TMEM165 impairs elongation of chondroitin- and heparan-sulfate glycosaminoglycan chains of proteoglycans and triggers early chondrocyte differentiation and hypertrophy.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Dec 20;13(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04458-1. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34930890 Free PMC article.
-
A dominant interference collagen X mutation disrupts hypertrophic chondrocyte pericellular matrix and glycosaminoglycan and proteoglycan distribution in transgenic mice.Am J Pathol. 2001 Dec;159(6):2257-69. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63076-3. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11733375 Free PMC article.
-
Progression and recapitulation of the chondrocyte differentiation program: cartilage matrix protein is a marker for cartilage maturation.Dev Biol. 1995 Nov;172(1):293-306. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.0024. Dev Biol. 1995. PMID: 7589809
-
Fate of growth plate hypertrophic chondrocytes: death or lineage extension?Dev Growth Differ. 2015 Feb;57(2):179-92. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12203. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Dev Growth Differ. 2015. PMID: 25714187 Review.
-
The cartilage extracellular matrix as a transient developmental scaffold for growth plate maturation.Matrix Biol. 2016 May-Jul;52-54:363-383. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.01.008. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Matrix Biol. 2016. PMID: 26807757 Review.
Cited by
-
CANT1 Is Involved in Collagen Fibrogenesis in Tendons by Regulating the Synthesis of Dermatan/Chondroitin Sulfate Attached to the Decorin Core Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 10;26(6):2463. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062463. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141107 Free PMC article.
-
XYLT1 Deficiency of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Impact on Osteogenic, Chondrogenic, and Adipogenic Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 30;26(15):7363. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157363. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806493 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA Degradation as a Therapeutic Solution for Mucopolysaccharidosis Type IIIC: Use of Antisense Oligonucleotides to Promote Downregulation of Heparan Sulfate Synthesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 1;26(3):1273. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031273. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941041 Free PMC article.
-
Xylosyltransferase-Deficiency in Human Dermal Fibroblasts Induces Compensatory Myofibroblast Differentiation and Long-Term ECM Reduction.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 4;12(3):572. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030572. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540185 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting FGFR3 signaling and drug repurposing for the treatment of SLC26A2-related chondrodysplasia in mouse model.J Orthop Translat. 2024 Jan 6;44:88-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2023.09.003. eCollection 2024 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2024. PMID: 38282752 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

