Asymptomatic viral infection is associated with lower host reproductive output in wild mink populations
- PMID: 37296209
- PMCID: PMC10251326
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36581-8
Asymptomatic viral infection is associated with lower host reproductive output in wild mink populations
Abstract
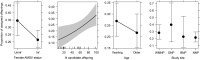
Many endemic viruses circulate in populations without hosts showing visible signs of disease, while still having the potential to alter host survival or reproduction. Aleutian Mink Disease Virus (AMDV) circulates in many American mink (Neogale vison) populations in its native and introduced ranges. In this study, we analysed how AMDV infection in female American mink affects the reproduction of a feral population. Females infected with AMDV delivered significantly smaller litters (5.8 pups) than uninfected females (6.3 pups), meaning their litter size was reduced by 8%. Larger females and yearling females had larger litters than smaller and older females. There were no significant differences in whole litter survival between infected and uninfected females; however, offspring survival until September or October within litters of infected females was 14% lower than that within those of uninfected females. This negative link between infection and reproductive output means that Aleutian disease could seriously affect the wild mink population. This study increases our understanding of the threats posed by the spread of viruses to wildlife from farm animals or humans, highlighting that viruses circulating in wildlife, even in the absence of clinical manifestation, can be important drivers of population dynamics in wildlife.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aleutian mink disease: Spatio-temporal variation of prevalence and influence on the feral American mink.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021 Jul;68(4):2556-2570. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13928. Epub 2020 Dec 20. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2021. PMID: 33197283 Free PMC article.
-
PREVALENCE OF ANTIBODY TO ALEUTIAN MINK DISEASE VIRUS IN EUROPEAN MINK (MUSTELA LUTREOLA) AND AMERICAN MINK (NEOVISON VISON) IN SPAIN.J Wildl Dis. 2016 Jan;52(1):22-32. doi: 10.7589/2015-04-082. Epub 2015 Nov 3. J Wildl Dis. 2016. PMID: 26528576
-
Testing for Aleutian mink disease virus in the river otter (Lontra canadensis) in sympatry with infected American mink (Neovison vison).J Wildl Dis. 2014 Jul;50(3):689-93. doi: 10.7589/2013-10-286. Epub 2014 May 7. J Wildl Dis. 2014. PMID: 24807350
-
AMDV Vaccine: Challenges and Perspectives.Viruses. 2021 Sep 14;13(9):1833. doi: 10.3390/v13091833. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis of Aleutian disease caused by Aleutian mink disease virus: A literature review with a perspective of genomic breeding for disease control in American mink (Neogale vison).Virus Res. 2023 Oct 15;336:199208. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199208. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 37633597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drivers Shaping Spillover of Aleutian Mink Disease Virus Introduced With American Mink Among Native Mustelids.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025 Feb 23;2025:3184679. doi: 10.1155/tbed/3184679. eCollection 2025. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025. PMID: 40302756 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Aleutian Mink Disease Virus (AMDV) in Free-Ranging American Mink from Biebrza and Narew National Parks (Poland)-An Epidemiological Concern.Animals (Basel). 2024 Sep 5;14(17):2584. doi: 10.3390/ani14172584. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272370 Free PMC article.
-
A developed TaqMan probe-based qPCR was used to quantify the distribution of AMDV in various tissues of infected mink and its prevalence in northern China.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jan 7;11:1498481. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1498481. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 39840339 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

