Role of Imaging in the Management of Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Lung Involvement Admitted to the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37296708
- PMCID: PMC10252607
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13111856
Role of Imaging in the Management of Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Lung Involvement Admitted to the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review
Abstract
During the waves of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, emergency departments were overflowing with patients suffering with suspected medical or surgical issues. In these settings, healthcare staff should be able to deal with different medical and surgical scenarios while protecting themselves against the risk of contamination. Various strategies were used to overcome the most critical issues and guarantee quick and efficient diagnostic and therapeutic charts. The use of saliva and nasopharyngeal swab Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAAT) in the diagnosis of COVID-19 was one of the most adopted worldwide. However, NAAT results were slow to report and could sometimes create significant delays in patient management, especially during pandemic peaks. On these bases, radiology has played and continues to play an essential role in detecting COVID-19 patients and solving differential diagnosis between different medical conditions. This systematic review aims to summarize the role of radiology in the management of COVID-19 patients admitted to emergency departments by using chest X-rays (CXR), computed tomography (CT), lung ultrasounds (LUS), and artificial intelligence (AI).
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; X-ray computed; artificial intelligence; coronavirus; infections; radiography; tomography; ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
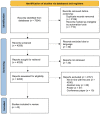
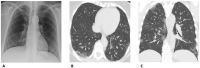

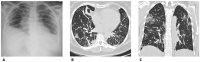
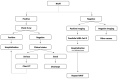
References
-
- [(accessed on 15 May 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Ochani R., Asad A., Yasmin F., Shaikh S., Khalid H., Batra S., Sohail M.R., Mahmood S.F., Ochani R., Arshad M.H., et al. COVID-19 Pandemic: From Origins to Outcomes. A Comprehensive Review of Viral Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnostic Evaluation, and Management. Infez. Med. 2021;29:20–36. - PubMed
-
- Butler-Laporte G., Lawandi A., Schiller I., Yao M., Dendukuri N., McDonald E.G., Lee T.C. Comparison of Saliva and Nasopharyngeal Swab Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing for Detection of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021;181:353–360. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.8876. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- [(accessed on 20 February 2023)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

