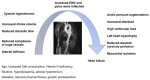
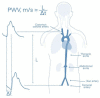
Arterial Stiffness as a Surrogate Marker of Cardiovascular Disease and Atherosclerosis in Patients with Arthritides and Connective Tissue Diseases: A Literature Review
- PMID: 37296720
- PMCID: PMC10252997
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13111870
Arterial Stiffness as a Surrogate Marker of Cardiovascular Disease and Atherosclerosis in Patients with Arthritides and Connective Tissue Diseases: A Literature Review
Abstract
The increased cardiovascular (CV) risk among patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases, such as arthritides and connective tissue diseases, has been extensively documented. From a pathophysiological standpoint, systemic inflammation in the context of the disease can lead to endothelial dysfunction, accelerated atherosclerosis, and structural changes in vessel walls, which, in turn, are associated with exaggerated CV morbidity and mortality. In addition to these abnormalities, the increased prevalence of traditional CV risk factors, such as obesity, dyslipidemia, arterial hypertension, and impaired glucose metabolism, can further worsen the status of and overall prognosis for CV in rheumatic patients. However, data on appropriate CV screening methods for patients with systemic autoimmune diseases are scarce, and traditional algorithms may lead to an underestimation of the true CV risk. The reason for this is that these calculations were developed for the general population and thus do not take into account the effect of the inflammatory burden, as well as other chronic-disease-associated CV risk factors. In recent years, different research groups, including ours, have examined the value of different CV surrogate markers, including carotid sonography, carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity, and flow-mediated arterial dilation, in the assessment of CV risk in healthy and rheumatic populations. In particular, arterial stiffness has been thoroughly examined in a number of studies, showing high diagnostic and predictive value for the occurrence of CV events. To this end, the present narrative review showcases a series of studies examining aortic and peripheral arterial stiffness as surrogates of all-cause CV disease and atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis, as well as in systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis. Moreover, we discuss the associations of arterial stiffness with clinical, laboratory, and disease-specific parameters.
Keywords: arterial stiffness; atherosclerosis; augmentation index; cardiovascular disease; psoriatic arthritis; pulse wave velocity; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic lupus erythematosus; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arterial Stiffness as a Surrogate Marker of Cardiovascular Disease and Atherosclerosis in Patients with Vasculitides: A Literature Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Dec 5;13(24):3603. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13243603. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular markers of microangiopathy and their possible association with cardiovascular risk in patients with systemic inflammatory rheumatic diseases: a systematic review.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 15;16:1543157. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1543157. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40303406 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial stiffness, the hidden face of cardiovascular risk in autoimmune and chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases.Autoimmun Rev. 2021 Sep;20(9):102891. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102891. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Autoimmun Rev. 2021. PMID: 34229047 Review.
-
Novel Surrogate Markers of Cardiovascular Risk in the Setting of Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: Current Data and Implications for the Future.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 30;9:820263. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.820263. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35847825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of mean blood pressure on arterial stiffening and endothelial dysfunction in women with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.Medicina (Kaunas). 2010;46(8):522-30. Medicina (Kaunas). 2010. PMID: 20966628
Cited by
-
Arterial Stiffness as a Surrogate Marker of Cardiovascular Disease and Atherosclerosis in Patients with Vasculitides: A Literature Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Dec 5;13(24):3603. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13243603. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic mistimed feeding results in renal fibrosis and disrupted circadian blood pressure rhythms.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Nov 1;327(5):F683-F696. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00047.2024. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39205662
-
Under-recognized cardiovascular risk enhancers in women: A call to rethink clinical assessment on risk stratification.Am J Prev Cardiol. 2025 Feb 11;21:100942. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2025.100942. eCollection 2025 Mar. Am J Prev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40060172 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular markers of microangiopathy and their possible association with cardiovascular risk in patients with systemic inflammatory rheumatic diseases: a systematic review.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 15;16:1543157. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1543157. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40303406 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis and cardiovascular risk: associated and protective factors.An Bras Dermatol. 2025 May-Jun;100(3):456-461. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2024.07.013. Epub 2025 Mar 12. An Bras Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40082144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Restivo V., Candiloro S., Daidone M., Norrito R., Cataldi M., Minutolo G., Caracci F., Fasano S., Ciccia F., Casuccio A., et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular risk in rheumatological disease: Symptomatic and non-symptomatic events in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022;21:102925. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102925. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources