Rapid Whole-Body FDG PET/MRI in Oncology Patients: Utility of Combining Bayesian Penalised Likelihood PET Reconstruction and Abbreviated MRI
- PMID: 37296723
- PMCID: PMC10252718
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13111871
Rapid Whole-Body FDG PET/MRI in Oncology Patients: Utility of Combining Bayesian Penalised Likelihood PET Reconstruction and Abbreviated MRI
Abstract
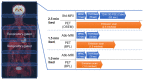
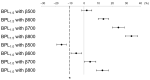
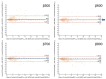
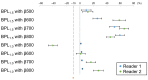
This study evaluated the diagnostic value of a rapid whole-body fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) approach, combining Bayesian penalised likelihood (BPL) PET with an optimised β value and abbreviated MRI (abb-MRI). The study compares the diagnostic performance of this approach with the standard PET/MRI that utilises ordered subsets expectation maximisation (OSEM) PET and standard MRI (std-MRI). The optimal β value was determined by evaluating the noise-equivalent count (NEC) phantom, background variability, contrast recovery, recovery coefficient, and visual scores (VS) for OSEM and BPL with β100-1000 at 2.5-, 1.5-, and 1.0-min scans, respectively. Clinical evaluations were conducted for NECpatient, NECdensity, liver signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), lesion maximum standardised uptake value, lesion signal-to-background ratio, lesion SNR, and VS in 49 patients. The diagnostic performance of BPL/abb-MRI was retrospectively assessed for lesion detection and differentiation in 156 patients using VS. The optimal β values were β600 for a 1.5-min scan and β700 for a 1.0-min scan. BPL/abb-MRI at these β values was equivalent to OSEM/std-MRI for a 2.5-min scan. By combining BPL with optimal β and abb-MRI, rapid whole-body PET/MRI could be achieved in ≤1.5 min per bed position, while maintaining comparable diagnostic performance to standard PET/MRI.
Keywords: Bayesian penalised likelihood; PET/MRI; abbreviated MRI; fluorodeoxyglucose; image reconstruction; whole-body imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Huellner M.W., Appenzeller P., Kuhn F.P., Husmann L., Pietsch C.M., Burger I.A., Porto M., Delso G., von Schulthess G.K., Veit-Haibach P. Whole-body nonenhanced PET/MR versus PET/CT in the staging and restaging of cancers: Preliminary observations. Radiology. 2014;273:859–869. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14140090. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chilcott A.K., Bradley K.M., McGowan D.R. Effect of a Bayesian Penalized Likelihood PET Reconstruction Compared with Ordered Subset Expectation Maximisation on Clinical Image Quality Over a Wide Range of Patient Weights. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018;210:153–157. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.18060. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lindstrom E., Sundin A., Trampal C., Lindsjo L., Ilan E., Danfors T., Antoni G., Sorensen J., Lubberink M. Evaluation of Penalized-Likelihood Estimation Reconstruction on a Digital Time-of-Flight PET/CT Scanner for (18)F-FDG Whole-Body Examinations. J. Nucl. Med. 2018;59:1152–1158. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.200790. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

