Explainable AI for Retinoblastoma Diagnosis: Interpreting Deep Learning Models with LIME and SHAP
- PMID: 37296784
- PMCID: PMC10253103
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13111932
Explainable AI for Retinoblastoma Diagnosis: Interpreting Deep Learning Models with LIME and SHAP
Abstract
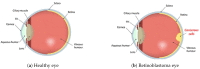
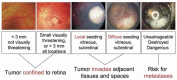
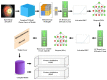
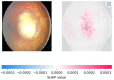
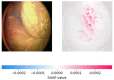
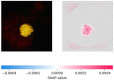
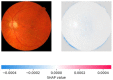
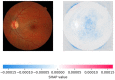
Retinoblastoma is a rare and aggressive form of childhood eye cancer that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent vision loss and even death. Deep learning models have shown promising results in detecting retinoblastoma from fundus images, but their decision-making process is often considered a "black box" that lacks transparency and interpretability. In this project, we explore the use of LIME and SHAP, two popular explainable AI techniques, to generate local and global explanations for a deep learning model based on InceptionV3 architecture trained on retinoblastoma and non-retinoblastoma fundus images. We collected and labeled a dataset of 400 retinoblastoma and 400 non-retinoblastoma images, split it into training, validation, and test sets, and trained the model using transfer learning from the pre-trained InceptionV3 model. We then applied LIME and SHAP to generate explanations for the model's predictions on the validation and test sets. Our results demonstrate that LIME and SHAP can effectively identify the regions and features in the input images that contribute the most to the model's predictions, providing valuable insights into the decision-making process of the deep learning model. In addition, the use of InceptionV3 architecture with spatial attention mechanism achieved high accuracy of 97% on the test set, indicating the potential of combining deep learning and explainable AI for improving retinoblastoma diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: InceptionV3; LIME; SHAP; deep learning; explainable AI; medical image analysis; retinoblastoma; transfer learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Interpretable AI for bio-medical applications.Complex Eng Syst. 2022 Dec;2(4):18. doi: 10.20517/ces.2022.41. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Complex Eng Syst. 2022. PMID: 37025127 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an ensemble CNN model with explainable AI for the classification of gastrointestinal cancer.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 25;19(6):e0305628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305628. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38917159 Free PMC article.
-
An Explainable AI Paradigm for Alzheimer's Diagnosis Using Deep Transfer Learning.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 5;14(3):345. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030345. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337861 Free PMC article.
-
Interpreting artificial intelligence models: a systematic review on the application of LIME and SHAP in Alzheimer's disease detection.Brain Inform. 2024 Apr 5;11(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40708-024-00222-1. Brain Inform. 2024. PMID: 38578524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Practical guide to SHAP analysis: Explaining supervised machine learning model predictions in drug development.Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Nov;17(11):e70056. doi: 10.1111/cts.70056. Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39463176 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The diagnostic and prognostic capability of artificial intelligence in spinal cord injury: A systematic review.Brain Spine. 2025 Feb 5;5:104208. doi: 10.1016/j.bas.2025.104208. eCollection 2025. Brain Spine. 2025. PMID: 40027293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Bovine, Porcine, and Sheep Muscle Using Interpretable Machine Learning Models.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;14(20):2947. doi: 10.3390/ani14202947. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457877 Free PMC article.
-
A review of emergent intelligent systems for the detection of Parkinson's disease.Biomed Eng Lett. 2023 Sep 20;13(4):591-612. doi: 10.1007/s13534-023-00319-2. eCollection 2023 Nov. Biomed Eng Lett. 2023. PMID: 37872986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interpretable prediction of 30-day mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis based on machine learning and SHAP.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024 Nov 5;24(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s12911-024-02741-7. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2024. PMID: 39501235 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing Retinal Vessel Morphology in MS Using Interpretable AI on Deep Learning-Segmented IR-SLO Images.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Aug 6;12(8):847. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12080847. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Association A. Retinoblastoma. [(accessed on 20 April 2023)]. Available online: https://www.aoa.org/healthy-eyes/eye-and-vision-conditions/retinoblastom....
-
- Berry J., Kim J., Damato B., Singh A. Clinical Ophthalmic Oncology: Retinoblastoma. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2019.
-
- Ramírez-Ortiz M., Lansingh V., Eckert K., Haik B., Phillips B., Bosch-Canto V., González-Pérez G., Villavicencio-Torres A., Etulain-González A. Systematic review of the current status of programs and general knowledge of diagnosis and management of retinoblastoma. BoletíN MéDico Del Hosp. Infant. MéXico (Engl. Ed.) 2017;74:41–54. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

