COVID-19 Lung Ultrasound Scores and Lessons from the Pandemic: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 37296825
- PMCID: PMC10252920
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13111972
COVID-19 Lung Ultrasound Scores and Lessons from the Pandemic: A Narrative Review
Abstract
The WHO recently declared that COVID-19 no longer constitutes a public health emergency of international concern; however, lessons learned through the pandemic should not be left behind. Lung ultrasound was largely utilized as a diagnostic tool thanks to its feasibility, easy application, and the possibility to reduce the source of infection for health personnel. Lung ultrasound scores consist of grading systems used to guide diagnosis and medical decisions, owning a good prognostic value. In the emergency context of the pandemic, several lung ultrasound scores emerged either as new scores or as modifications of pre-existing ones. Our aim is to clarify the key aspects of lung ultrasound and lung ultrasound scores to standardize their clinical use in a non-pandemic context. The authors searched on PubMed for articles related to "COVID-19", "ultrasound", and "Score" until 5 May 2023; other keywords were "thoracic", "lung", "echography", and "diaphragm". A narrative summary of the results was made. Lung ultrasound scores are demonstrated to be an important tool for triage, prediction of severity, and aid in medical decisions. Ultimately, the existence of numerous scores leads to a lack of clarity, confusion, and an absence of standardization.
Keywords: COVID-19; lung ultrasound; score.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
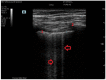


References
-
- Statement on the Fifteenth Meeting of the IHR (2005) Emergency Committee on the COVID-19 Pandemic. [(accessed on 5 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2023-statement-on-the-fifteenth-meet....
-
- Rizzetto F., Perillo N., Artioli D., Travaglini F., Cuccia A., Zannoni S., Tombini V., Di Domenico S.L., Albertini V., Bergamaschi M., et al. Correlation between lung ultrasound and chest CT patterns with estimation of pulmonary burden in COVID-19 patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021;138:109650. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109650. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

