Combination of High-Resolution Structures for the B Cell Receptor and Co-Receptors Provides an Understanding of Their Interactions with Therapeutic Antibodies
- PMID: 37296844
- PMCID: PMC10251933
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15112881
Combination of High-Resolution Structures for the B Cell Receptor and Co-Receptors Provides an Understanding of Their Interactions with Therapeutic Antibodies
Abstract
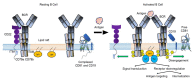
B cells are central to the adaptive immune response, providing long lasting immunity after infection. B cell activation is mediated by a cell surface B cell receptor (BCR) following recognition of an antigen. BCR signaling is modulated by several co-receptors including CD22 and a complex that contains CD19 and CD81. Aberrant signaling through the BCR and co-receptors promotes the pathogenesis of several B cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases. Treatment of these diseases has been revolutionized by the development of monoclonal antibodies that bind to B cell surface antigens, including the BCR and its co-receptors. However, malignant B cells can escape targeting by several mechanisms and until recently, rational design of antibodies has been limited by the lack of high-resolution structures of the BCR and its co-receptors. Herein we review recently determined cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and crystal structures of the BCR, CD22, CD19 and CD81 molecules. These structures provide further understanding of the mechanisms of current antibody therapies and provide scaffolds for development of engineered antibodies for treatment of B cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: B cell; B cell receptor; CD19; CD22; CD81; cryo-electron microscopy; crystallography; monoclonal antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

