Metastatic Breast Cancer: Review of Emerging Nanotherapeutics
- PMID: 37296869
- PMCID: PMC10251990
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15112906
Metastatic Breast Cancer: Review of Emerging Nanotherapeutics
Abstract
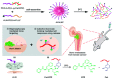
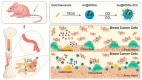
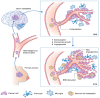
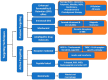
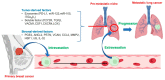
Metastases of breast cancer (BC) are often referred to as stage IV breast cancer due to their severity and high rate of mortality. The median survival time of patients with metastatic BC is reduced to 3 years. Currently, the treatment regimens for metastatic BC are similar to the primary cancer therapeutics and are limited to conventional chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgery. However, metastatic BC shows organ-specific complex tumor cell heterogeneity, plasticity, and a distinct tumor microenvironment, leading to therapeutic failure. This issue can be successfully addressed by combining current cancer therapies with nanotechnology. The applications of nanotherapeutics for both primary and metastatic BC treatments are developing rapidly, and new ideas and technologies are being discovered. Several recent reviews covered the advancement of nanotherapeutics for primary BC, while also discussing certain aspects of treatments for metastatic BC. This review provides comprehensive details on the recent advancement and future prospects of nanotherapeutics designed for metastatic BC treatment, in the context of the pathological state of the disease. Furthermore, possible combinations of current treatment with nanotechnology are discussed, and their potential for future transitions in clinical settings is explored.
Keywords: breast cancer; metastasis; nanotherapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

