Chemo-Immunotherapy: A New Trend in Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 37296876
- PMCID: PMC10252089
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15112912
Chemo-Immunotherapy: A New Trend in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
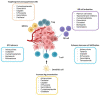
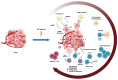
Chemotherapy has been the basis of advanced cancer treatment for decades. This therapy has largely been considered immunosuppressive, yet accumulated preclinical and clinical evidence shows that certain chemotherapeutic drugs, under defined conditions, may stimulate antitumor immunity and potentiate immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-based therapy. Its effectiveness has been highlighted by recent regulatory approvals of various combinations of chemotherapy with ICIs in several tumors, particularly in some difficult-to-treat cancers. This review discusses the immune modulatory properties of chemotherapy and how they may be harnessed to develop novel chemo-immunotherapy combinations. It also highlights the key determinants of the success of chemo-immunotherapy and provides an overview of the combined chemo-immunotherapies that have been clinically approved.
Keywords: NK cell; PD-1; T cell; chemotherapy; immune checkpoints; immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- West H., McCleod M., Hussein M., Morabito A., Rittmeyer A., Conter H.J., Kopp H.G., Daniel D., McCune S., Mekhail T., et al. Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower130): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:924–937. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30167-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

