Efficacy of Tango Argentino for Cancer-Associated Fatigue and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 37296883
- PMCID: PMC10251919
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15112920
Efficacy of Tango Argentino for Cancer-Associated Fatigue and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Persistent impairments of quality of life-in particular, cancer-associated fatigue-are a major limitation for breast cancer survivors. As physical activity and mindfulness interventions have been shown to be effective in reducing fatigue symptoms, we investigated the efficacy of a six-week Argentine tango program.
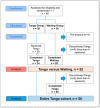
Methods: A randomized controlled trial was conducted with 60 breast cancer survivors diagnosed with stage I-III tumors 12-48 months prior to study enrollment and who had increased symptoms of fatigue. The participants were randomly assigned with a 1:1 allocation to either the tango or the waiting group. The treatment consisted of six weeks of supervised weekly one-hour tango group-sessions. Self-reported fatigue and further quality of life parameters were assessed at baseline and six weeks post-baseline. Longitudinal changes, correlations, Cohen's D (d) effect sizes, and association factors were also calculated.
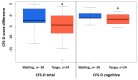
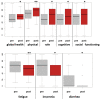
Results: Superiority of the tango intervention over the waiting list control was found in terms of improvement in fatigue (d = -0.64; 95%CI, -1.2 to -0.08; p = 0.03), especially cognitive fatigue. In addition, a superiority of the tango intervention over the waiting list was found in the improvement of diarrhea (d = -0.69; 95%CI, -1.25 to -0.13; p = 0.02). A pooled pre-post analysis of the 50 participants completing the six-week tango program revealed a close to 10% improvement of fatigue (p = 0.0003), insomnia (p = 0.008) and further quality of life outcomes. Adjusted multivariate linear regression analyses revealed the greatest improvements for participants who were more active in sports. In particular, survivors who received endocrine therapies, were obese, or had no prior dance experience seemed to especially benefit from the tango program.
Conclusions: This randomized controlled trial demonstrated that a six-week Argentine tango program improves fatigue in breast cancer survivors. Further trials are warranted to determine whether such improvements lead to better long-term clinical outcomes.
Trial registration: trial registration number DRKS00021601. Retrospectively registered on 21 August 2020.
Keywords: breast cancer; dance; fatigue; integrative oncology; physical activities; quality of life; supportive care; tango Argentino.
Conflict of interest statement
FS reports grants from Helixor Heilmittel GmbH (travel costs and honoraria for speaking), grants from AstraZeneca (travel costs and honoraria for speaking), grants from Abnoba GmbH, and grants from Iscador AG outside the submitted work. JG reports grants from Roche, Siemens, mte, and Celgene (travel costs and honoraria for speaking) outside the submitted work. HM is a member of the board of directors of Weleda AG, a member of the Network Arbeitsgemeinschaft der Wissenschaftlichen Fachgesellschaften (AWMF e.V.) guideline committee for integrative oncology (Guideline for Complementary Medicine in the Treatment of Oncological Patients) and has an endowed professorship at the Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, which is financed by the Software AG Foundation outside the submitted work. The other authors have declared that no competing interests exist. No payment was received for any other aspects of the submitted work. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. There are no other relationships/conditions/circumstances that present a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cella D., Peterman A., Passik S., Jacobsen P., Breitbart W. Progress toward guidelines for the management of fatigue. Oncology. 1998;12:369–377. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

