CAR-T Cells Immunotherapies for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Recent Advances
- PMID: 37296906
- PMCID: PMC10252035
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15112944
CAR-T Cells Immunotherapies for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Recent Advances
Abstract
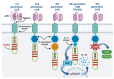
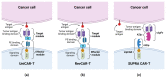
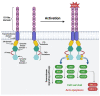
In order to increase the effectiveness of cancer therapies and extend the long-term survival of patients, more and more often, in addition to standard treatment, oncological patients receive also targeted therapy, i.e., CAR-T cells. These cells express a chimeric receptor (CAR) that specifically binds an antigen present on tumor cells, resulting in tumor cell lysis. The use of CAR-T cells in the therapy of relapsed and refractory B-type acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) resulted in complete remission in many patients, which prompted researchers to conduct tests on the use of CAR-T cells in the treatment of other hematological malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). AML is associated with a poorer prognosis compared to ALL due to a higher risk of relapse caused by the development of resistance to standard treatment. The 5-year relative survival rate in AML patients was estimated at 31.7%. The objective of the following review is to present the mechanism of action of CAR-T cells, and discuss the latest findings on the results of anti-CD33, -CD123, -FLT3 and -CLL-1 CAR-T cell therapy, the emerging challenges as well as the prospects for the future.
Keywords: AML; CAR-T; CD123; CD33; CLL-1; FLT3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

