Precision Medicine to Treat Urothelial Carcinoma-The Way Forward
- PMID: 37296985
- PMCID: PMC10252480
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15113024
Precision Medicine to Treat Urothelial Carcinoma-The Way Forward
Abstract
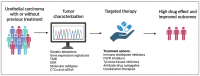
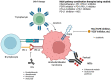
The treatment of urothelial carcinoma (UC) is challenging given its molecular heterogeneity and variable response to current therapies. To address this, many tools, including tumor biomarker assessment and liquid biopsies, have been developed to predict prognosis and treatment response. Approved therapeutic modalities for UC currently include chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and antibody drug conjugates. Ongoing investigations to improve the treatment of UC include the search for actionable alterations and the testing of novel therapies. An important objective in recent studies has been to increase efficacy while decreasing toxicity by taking into account unique patient and tumor-related factors-an endeavor called precision medicine. The aim of this review is to highlight advancements in the treatment of UC, describe ongoing clinical trials, and identify areas for future study in the context of precision medicine.
Keywords: biomarkers; immunotherapy; precision medicine; targeted therapy; urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted therapies: Expanding the role of FGFR3 inhibition in urothelial carcinoma.Urol Oncol. 2022 Feb;40(2):25-36. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2021.10.003. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Urol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34840077 Review.
-
Current Strategies and Novel Therapeutic Approaches for Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 2;12(6):1449. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061449. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32498352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increasing Biomarker Guidance in the Treatment of Urothelial Carcinoma: Systematic Review of International Clinical Trials.Urol Int. 2023;107(5):480-488. doi: 10.1159/000527879. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Urol Int. 2023. PMID: 36630942
-
The evolving role of checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of urothelial carcinoma.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Jan;89(1):93-113. doi: 10.1111/bcp.15504. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 35997657 Review.
-
Emerging biomarkers and targeted therapies in urothelial carcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Jun;6(12):250. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.05.49. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30069452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advancing Leukemia Management Through Liquid Biopsy: Insights into Biomarkers and Clinical Utility.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 25;17(9):1438. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091438. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contemporary Molecular Markers for Predicting Systemic Treatment Response in Urothelial Bladder Cancer: A Narrative Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 1;16(17):3056. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173056. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E-learning pills on immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma: The E-PIMUC program for continuing medical education.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 22;15:1380954. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1380954. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39239658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vandekerkhove G., Lavoie J.M., Annala M., Murtha A.J., Sundahl N., Walz S., Sano T., Taavitsainen S., Ritch E., Fazli L., et al. Plasma ctDNA is a tumor tissue surrogate and enables clinical-genomic stratification of metastatic bladder cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:184. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20493-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soave A., Riethdorf S., Dahlem R., von Amsberg G., Minner S., Weisbach L., Engel O., Fisch M., Pantel K., Rink M. A nonrandomized, prospective, clinical study on the impact of circulating tumor cells on outcomes of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder patients treated with radical cystectomy with or without adjuvant chemotherapy. Int. J. Cancer. 2017;140:381–389. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30445. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

