Proteins and Minerals in Whey Protein Supplements
- PMID: 37297488
- PMCID: PMC10252490
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12112238
Proteins and Minerals in Whey Protein Supplements
Abstract
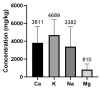
Sports nutrition supplementation is a widespread practice. Whey protein supplements contribute not only to protein intake but also to dietary exposure to minerals. The labelling present provides the percentage of protein and rarely refers to other components, such as potentially toxic elements such as B, Cu, Mo, Zn, and V that present tolerable upper intake levels set by the European Food Safety Authority. The percentage of protein declared on supplement labelling was checked using the Kjeldahl method, and the levels of Ca, Mg, K, Na, Ba, B, Co, Cu, Cr, Sr, Fe, Li, Mn, Mo, Ni, V, Zn, and Al were analyzed by ICP-OES with the aim of characterizing the protein and mineral contents of isolate and concentrate whey protein supplements representative of the European market. The protein content was 70.9% (18-92.3%) and statistically significant differences were observed between the declared and real protein percentages. Among the minerals, K (4689.10 mg/kg) and Ca (3811.27 mg/kg) presented the highest levels, whereas Co (0.07 mg/kg) and V (0.04 mg/kg) showed the lowest levels. It was concluded that the quality and safety of these products needs to be monitored and regulated. A high degree of non-compliance with labelling claims was detected. Furthermore, the contributions to the recommended and tolerable intakes among regular consumers need to be assessed.
Keywords: chemical elements; potentially toxic elements; protein supplements; proteins; whey protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whey Protein Dietary Supplements: Metal Exposure Assessment and Risk Characterization.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 11;15(16):3543. doi: 10.3390/nu15163543. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37630733 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the coal mining-contaminated soil on the food safety in Shaanxi, China.Environ Geochem Health. 2019 Jun;41(3):1521-1544. doi: 10.1007/s10653-018-0233-6. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Environ Geochem Health. 2019. PMID: 30600450
-
[Correlation of mineral elements between milled and brown rice and soils in Yunnan studied by ICP-AES].Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2009 May;29(5):1413-7. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2009. PMID: 19650503 Chinese.
-
The North/South Ireland Food Consumption Survey: mineral intakes in 18-64-year-old adults.Public Health Nutr. 2001 Oct;4(5A):1081-8. doi: 10.1079/phn2001189. Public Health Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11820921
-
Minerals in edible seaweed: health benefits and food safety issues.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(6):1592-1607. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1844637. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33203217 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the water source and formation process of Huangshui in solid-state fermentation.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 14;34(3):665-675. doi: 10.1007/s10068-024-01668-z. eCollection 2025 Feb. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39958167 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pH, Reducing Sugars, and Protein on Roasted Sunflower Seed Aroma Volatiles.Foods. 2023 Nov 17;12(22):4155. doi: 10.3390/foods12224155. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38002212 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Trends in Bioavailability and Pharma-Nutraceutical Potential of Whey Bioactives.J Nutr Metab. 2024 Apr 10;2024:8455666. doi: 10.1155/2024/8455666. eCollection 2024. J Nutr Metab. 2024. PMID: 38633607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whey Protein Dietary Supplements: Metal Exposure Assessment and Risk Characterization.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 11;15(16):3543. doi: 10.3390/nu15163543. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37630733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acosta Carrasco M.R. La nutrición, suplementación e hidratación en el ámbito deportivo como base en el físico culturismo. [(accessed on 5 December 2022)];Talentos. 2020 7:31–47. doi: 10.33789/talentos.7.1.121. Available online: https://talentos.ueb.edu.ec/index.php/talentos/article/view/200/282. - DOI
-
- AOAC Official Methods of the Analysis of the AOAC. 15th ed. Association of the Official Analytical Chemist; Washington, DC, USA: 1990. pp. 237–273.
-
- Armendáriz-Anguiano A., Jimenez-Cruz A., Bacardi-Gascon M., Perez-Morales E. Efectividad del uso de suplementos de proteína en entrenamientos de fuerza: Revisión sistemática. [(accessed on 5 December 2022)];Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2010 60:113–118. Available online: https://www.alanrevista.org/ediciones/2010/2/art-1/ - PubMed
-
- Blasco Redondo R. Las ayudas ergogénicas nutricionales en el ámbito deportivo. Primera parte. Aspectos generales. [(accessed on 6 December 2022)];Nutr. Clínica Med. 2016 10:69–78. doi: 10.7400/NCM.2016.10.2.5038. Available online: http://www.aulamedica.es/nutricionclinicamedicina/pdf/5038.pdf. - DOI
-
- Elgammal S.M., Khorshed M.A., Ismail E.H. Determination of heavy metal content in whey protein samples from markets in Giza, Egypt, using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry: A probabilistic risk assessment study. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019;84:103300. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2019.103300. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials