EASY-NET Program: Methods and Preliminary Results of an Audit and Feedback Intervention in the Emergency Care for Acute Myocardial Infarction in the Lazio Region, Italy
- PMID: 37297791
- PMCID: PMC10252972
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11111651
EASY-NET Program: Methods and Preliminary Results of an Audit and Feedback Intervention in the Emergency Care for Acute Myocardial Infarction in the Lazio Region, Italy
Abstract
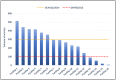
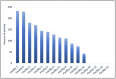
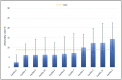
Within the EASY-NET network program (NET-2016-02364191), Work Package 1 Lazio evaluates the effectiveness of a structured audit and feedback (A&F) intervention compared with the web-based regional periodic publication of indicators in improving the appropriateness and timeliness of emergency healthcare for acute myocardial infarction (AMI). This work describes the A&F methodology and presents the results of the first feedback delivered. The intervention involves sending periodic reports via e-mail to participating hospitals. The feedback reports include a set of volume and quality (process and outcome) indicators, calculated by facility through the health information system of the Lazio Region and compared with regional mean, target values and values calculated for hospitals with similar volumes of activity. Health managers and clinicians of each participating hospital represent the "feedback recipients". They are invited to organize clinical and organizational audit meetings to identify possible critical issues in the care pathway and define, where necessary, improvement actions. A total of 16 facilities are involved. Twelve facilities present high volumes in all volume indicators, while three facilities present low volumes for each indicator. Concerning the quality indicators, four facilities do not present critical indicators or had average results, three facilities do not present critical indicators but show average results in at least one of the indicators and six facilities present a critical value for at least one of the indicators. The first report highlighted some critical issues in some facilities on several indicators. During the audit meetings, each facility analyzes these issues, defining appropriate improvement actions. The outcome of these actions will be monitored through subsequent reporting to support the continuous care quality improvement process.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; audit and feedback; emergency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Agenzia Nazionale per i Servizi Sanitari Regionali (AGENAS) Programma Nazionale Esiti. [(accessed on 10 May 2022)];2021 Available online: https://pne.agenas.it/
-
- Flottorp S.A., Jamtvedt G., Gibis B., Mckee M. Using audit and feedback to health professionals to improve the quality and safety of health care; Proceedings of the Belgian EU Presidency Conference on Investing in Europe’s Health Workforce of Tomorrow: Scope for Innovation and Collaboration; La Hulpe, Belgium. 9–10 September 2010; [(accessed on 15 September 2022)]. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/332014?show=full.
-
- Ivers N., Jamtvedt G., Flottorp S., Young J.M., Odgaard-Jensen J., French S.D., O’Brien M.A., Johansen M., Grimshaw J., Oxman A.D. Audit and feedback: Effects on professional practice and healthcare outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012;6:1465–1858. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000259.pub3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

