Inducible and Conditional Activation of Adult Neurogenesis Rescues Cadmium-Induced Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Deficits in ApoE4-KI Mice
- PMID: 37298071
- PMCID: PMC10253189
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24119118
Inducible and Conditional Activation of Adult Neurogenesis Rescues Cadmium-Induced Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Deficits in ApoE4-KI Mice
Abstract
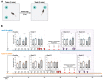
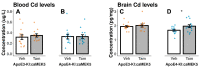
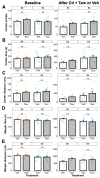
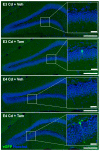
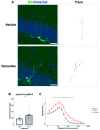
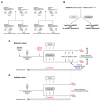
The apolipoprotein E (ApoE) gene is a genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease, in which ε4 allele carriers have increased risk compared to the common ε3 carriers. Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic heavy metal and a potential neurotoxicant. We previously reported a gene-environment interaction (GxE) effect between ApoE4 and Cd that accelerates or increases the severity of the cognitive decline in ApoE4-knockin (ApoE4-KI) mice exposed to 0.6 mg/L CdCl2 through drinking water compared to control ApoE3-KI mice. However, the mechanisms underlying this GxE effect are not yet defined. Because Cd impairs adult neurogenesis, we investigated whether genetic and conditional stimulation of adult neurogenesis can functionally rescue Cd-induced cognitive impairment in ApoE4-KI mice. We crossed either ApoE4-KI or ApoE3-KI to an inducible Cre mouse strain, Nestin-CreERTM:caMEK5-eGFPloxP/loxP (designated as caMEK5), to generate ApoE4-KI:caMEK5 and ApoE3-KI:caMEK5. Tamoxifen administration in these mice genetically and conditionally induces the expression of caMEK5 in adult neural stem/progenitor cells, enabling the stimulation of adult neurogenesis in the brain. Male ApoE4-KI:caMEK5 and ApoE3-KI:caMEK5 mice were exposed to 0.6 mg/L CdCl2 throughout the experiment, and tamoxifen was administered once Cd-induced impairment in spatial working memory was consistently observed. Cd exposure impaired spatial working memory earlier in ApoE4-KI:caMEK5 than in ApoE3-KI:caMEK5 mice. In both strains, these deficits were rescued after tamoxifen treatment. Consistent with these behavioral findings, tamoxifen treatment enhanced adult neurogenesis by increasing the morphological complexity of adult-born immature neurons. These results provide evidence for a direct link between impaired spatial memory and adult neurogenesis in this GxE model.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; adult neurogenesis; cadmium; gene–environment interaction; neurotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

