Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of R2R3-MYB Genes Response to Saline-Alkali Stress in Quinoa
- PMID: 37298082
- PMCID: PMC10252952
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24119132
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of R2R3-MYB Genes Response to Saline-Alkali Stress in Quinoa
Abstract
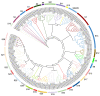
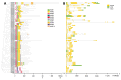
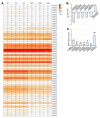
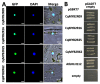
Soil saline-alkalization inhibits plant growth and development and seriously affects crop yields. Over their long-term evolution, plants have formed complex stress response systems to maintain species continuity. R2R3-MYB transcription factors are one of the largest transcription factor families in plants, widely involved in plant growth and development, metabolism, and stress response. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.), as a crop with high nutritional value, is tolerant to various biotic and abiotic stress. In this study, we identified 65 R2R3-MYB genes in quinoa, which are divided into 26 subfamilies. In addition, we analyzed the evolutionary relationships, protein physicochemical properties, conserved domains and motifs, gene structure, and cis-regulatory elements of CqR2R3-MYB family members. To investigate the roles of CqR2R3-MYB transcription factors in abiotic stress response, we performed transcriptome analysis to figure out the expression file of CqR2R3-MYB genes under saline-alkali stress. The results indicate that the expression of the six CqMYB2R genes was altered significantly in quinoa leaves that had undergone saline-alkali stress. Subcellular localization and transcriptional activation activity analysis revealed that CqMYB2R09, CqMYB2R16, CqMYB2R25, and CqMYB2R62, whose Arabidopsis homologues are involved in salt stress response, are localized in the nucleus and exhibit transcriptional activation activity. Our study provides basic information and effective clues for further functional investigation of CqR2R3-MYB transcription factors in quinoa.
Keywords: CqMYB2Rs; metabolism; stress response; transcription factors; transcriptome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders have no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of the R2R3-MYB gene family in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) under abiotic stress.Funct Plant Biol. 2024 Feb;51:FP23261. doi: 10.1071/FP23261. Funct Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38417846
-
Identification and expression analysis of the CqSnRK2 gene family and a functional study of the CqSnRK2.12 gene in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.).BMC Genomics. 2022 May 24;23(1):397. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08626-1. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35610576 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic analysis, and expression profiles of trihelix transcription factor family genes in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) under abiotic stress conditions.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jul 10;23(1):499. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08726-y. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35810309 Free PMC article.
-
Function of MYB domain transcription factors in abiotic stress and epigenetic control of stress response in plant genome.Plant Signal Behav. 2016;11(1):e1117723. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2015.1117723. Plant Signal Behav. 2016. PMID: 26636625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MYB transcription factors and their roles in the male reproductive development of flowering plants.Plant Sci. 2023 Oct;335:111811. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2023.111811. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37574139 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of MYB Transcription Factor Family in Response to Various Abiotic Stresses in Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 18;25(18):10048. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810048. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337532 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide identification of LcC2DPs gene family in Lotus corniculatus provides insights into regulatory network in response to abiotic stresses.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 18;15(1):13380. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97896-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40251318 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Family Based on Amaranthus tricolor Genome and AtrMYB72 Promoting Betalain Biosynthesis by Directly Activating AtrCYP76AD1 Expression.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jan 22;14(3):324. doi: 10.3390/plants14030324. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39942886 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of YABBY Genes in Chenopodium quinoa.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 19;14(11):2103. doi: 10.3390/genes14112103. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003046 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factors in Casuarina equisetifolia and the function analysis of CeqWRKY11 in response to NaCl/NaHCO3 stresses.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 May 8;24(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04889-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38714947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaiwen G., Zisong X., Yuze H., Qi S., Yue W., Yanhui C., Jiechen W., Wei L., Huihui Z. Effects of salt concentration, pH, and their interaction on plant growth, nutrient uptake, and photochemistry of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) leaves. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020;15:1832373. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1832373. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang L., Seki K., Miyazaki T., Ishihama Y. The causes of soil alkalinization in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2009;7:259–270. doi: 10.1007/s10333-009-0166-x. - DOI
-
- Dhaka M. A comprehensive study on core enzymes involved in starch metabolism in the model nutricereal, foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) J. Cereal Sci. 2021;97:103153. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2020.103153. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

