Faujasite-Type Zeolite Obtained from Ecuadorian Clay as a Support of ZnTiO3/TiO2 NPs for Cyanide Removal in Aqueous Solutions
- PMID: 37298234
- PMCID: PMC10252533
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24119281
Faujasite-Type Zeolite Obtained from Ecuadorian Clay as a Support of ZnTiO3/TiO2 NPs for Cyanide Removal in Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
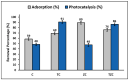
In this study, zeolites prepared by the hydrothermal method from Ecuadorian clay were combined with the precursor clay and with the semiconductor ZnTiO3/TiO2 prepared by the sol-gel method to adsorb and photodegrade cyanide species from aqueous solutions. These compounds were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-rays, point of zero charge, and specific surface area. The adsorption characteristics of the compounds were measured using batch adsorption experiments as a function of pH, initial concentration, temperature, and contact time. The Langmuir isotherm model and the pseudo-second-order model fit the adsorption process better. The equilibrium state in the reaction systems at pH = 7 was reached around 130 and 60 min in the adsorption and photodegradation experiments, respectively. The maximum cyanide adsorption value (73.37 mg g-1) was obtained with the ZC compound (zeolite + clay), and the maximum cyanide photodegradation capacity (90.7%) under UV light was obtained with the TC compound (ZnTiO3/TiO2 + clay). Finally, the reuse of the compounds in five consecutive treatment cycles was determined. The results reflect that the compounds synthesized and adapted to the extruded form could potentially be used for the removal of cyanide from wastewater.
Keywords: ZnTiO3/TiO2; adsorption; clay; cyanide; faujasite; nanoparticles; photocatalysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures














References
-
- Dwivedi N., Dwivedi S., Adetunji C.O. Efficacy of Microorganisms in the Removal of Toxic Materials from Industrial Effluents. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2021. pp. 325–358. - DOI
-
- Ravuru S.S., Jana A., De S. Cyanide removal from blast furnace effluent using layered double hydroxide based mixed matrix beads: Batch and fixed bed study. J. Clean. Prod. 2022;371:133634. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133634. - DOI
-
- Aranguri LLerena G., Reyes López I.A. Cyanide Degradation from Mining Effluent Using Two Reagents: Sodium Metabisulphite and the Metabisulphite Mixture with Hydrogen Peroxide. Tecciencia. 2019;13:1–9. doi: 10.18180/tecciencia.2018.25.1. - DOI
-
- Aranguri-Llerena G., Reyes-Lázaro W. Adsorption of cyanide contained in aqueous solution using activated carbon obtained from coffee residue: Absorption efficiency, equilibrium and kinetic model. Sci. Agropecu. 2019;10:315–325. doi: 10.17268/sci.agropecu.2019.03.01. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

