A Unique Mode of Coenzyme A Binding to the Nucleotide Binding Pocket of Human Metastasis Suppressor NME1
- PMID: 37298313
- PMCID: PMC10253429
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24119359
A Unique Mode of Coenzyme A Binding to the Nucleotide Binding Pocket of Human Metastasis Suppressor NME1
Abstract
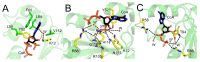
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a key cellular metabolite which participates in diverse metabolic pathways, regulation of gene expression and the antioxidant defense mechanism. Human NME1 (hNME1), which is a moonlighting protein, was identified as a major CoA-binding protein. Biochemical studies showed that hNME1 is regulated by CoA through both covalent and non-covalent binding, which leads to a decrease in the hNME1 nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) activity. In this study, we expanded the knowledge on previous findings by focusing on the non-covalent mode of CoA binding to the hNME1. With X-ray crystallography, we solved the CoA bound structure of hNME1 (hNME1-CoA) and determined the stabilization interactions CoA forms within the nucleotide-binding site of hNME1. A hydrophobic patch stabilizing the CoA adenine ring, while salt bridges and hydrogen bonds stabilizing the phosphate groups of CoA were observed. With molecular dynamics studies, we extended our structural analysis by characterizing the hNME1-CoA structure and elucidating possible orientations of the pantetheine tail, which is absent in the X-ray structure due to its flexibility. Crystallographic studies suggested the involvement of arginine 58 and threonine 94 in mediating specific interactions with CoA. Site-directed mutagenesis and CoA-based affinity purifications showed that arginine 58 mutation to glutamate (R58E) and threonine 94 mutation to aspartate (T94D) prevent hNME1 from binding to CoA. Overall, our results reveal a unique mode by which hNME1 binds CoA, which differs significantly from that of ADP binding: the α- and β-phosphates of CoA are oriented away from the nucleotide-binding site, while 3'-phosphate faces catalytic histidine 118 (H118). The interactions formed by the CoA adenine ring and phosphate groups contribute to the specific mode of CoA binding to hNME1.
Keywords: CoAlation; NDPK-A structure; NM23-H1; NME1; X-ray crystallography; coenzyme A; metastasis suppressor; molecular dynamics; nucleotide binding; protein-metabolite regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinases Are ATP-Regulated Carriers of Short-Chain Acyl-CoAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7528. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147528. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of metastasis suppressor NME1 by a key metabolic cofactor coenzyme A.Redox Biol. 2021 Aug;44:101978. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101978. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Redox Biol. 2021. PMID: 33903070 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of Human NME1 in Neuronal Differentiation of Porcine Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Application of NB-hNME1 as a Human NME1 Suppressor.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 11;22(22):12194. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212194. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830075 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis suppressor NM23 limits oxidative stress in mammals by preventing activation of stress-activated protein kinases/JNKs through its nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity.FASEB J. 2017 Apr;31(4):1531-1546. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600705R. Epub 2017 Jan 11. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28077425
-
Structure, Folding and Stability of Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 16;21(18):6779. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186779. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32947863 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial NME6: A Paradigm Change within the NME/NDP Kinase Protein Family?Cells. 2024 Jul 30;13(15):1278. doi: 10.3390/cells13151278. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinases Are ATP-Regulated Carriers of Short-Chain Acyl-CoAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7528. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147528. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A (NME1) catalyses its own oligophosphorylation.Nat Chem. 2025 Aug 20. doi: 10.1038/s41557-025-01915-8. Online ahead of print. Nat Chem. 2025. PMID: 40835738
-
Investigating the Regulation of Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase 1 by CoAlation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 11;25(16):8747. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168747. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201434 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine Phosphorylation: Protein Kinases and Phosphatases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 21;25(14):7975. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147975. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063217 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

