Volatile Composition and Classification of Paeonia lactiflora Flower Aroma Types and Identification of the Fragrance-Related Genes
- PMID: 37298360
- PMCID: PMC10253308
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24119410
Volatile Composition and Classification of Paeonia lactiflora Flower Aroma Types and Identification of the Fragrance-Related Genes
Abstract
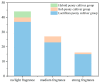
Flower scent is one of the main ornamental characteristics of herbaceous peony, and the improvement of flower fragrance is a vital objective of herbaceous peony breeding. In this study, 87 herbaceous peony cultivars were divided into three groups (no/light fragrance, medium fragrance, and strong fragrance) based on their sensory evaluation scores, and 16 strong fragrance cultivars and one no fragrance cultivar were selected for subsequent analysis. Sixty-eight volatile components were detected in these 17 cultivars based on solid-phase microextraction (SPME) and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS), and 26 types were identified as important scent components. They were composed of terpenoids, benzenoids/phenylpropanoids, and fatty acid derivatives. According to the content and odor threshold of these main aroma components, the characteristic aroma substances of herbaceous peony were identified, including linalool, geraniol, citronellol, and phenylethyl alcohol (2-PE). The cultivars of strong scented herbaceous peony were divided into three types: rose scent, lily scent, and mixed scent. We explored the possible key genes of characteristic aroma substances in herbaceous peony petals with different odors through the qRT-PCR. The key genes encoding monoterpene biosynthesis were found to be PlDXS2, PlDXR1, PlMDS1, PlHDR1, PlGPPS3, and PlGPPS4. In addition, the linalool synthase (LIS) gene and the geraniol synthase (GES) gene were also found. PlAADC1, PlPAR1, and PlMAO1, related to the biosynthesis of 2-PE were detected, and the synthetic pathway of 2-PE was speculated. In conclusion, these findings revealed that the difference in gene expression of monoterpene and 2-PE synthesis pathway was related to the difference in the fragrance of herbaceous peony. This study explored the releasing pathway of herbaceous peony characteristic aroma substances and provided key genetic resources for fragrance improvement.
Keywords: floral fragrance; herbaceous peony; monoterpenes; phenylethyl alcohol; volatiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Transcriptome and volatile compounds analyses of floral development provide insight into floral scent formation in Paeonia lactiflora 'Wu Hua Long Yu'.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 16;15:1303156. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1303156. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38434428 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome sequencing reveals terpene biosynthesis pathway genes accounting for volatile terpene of tree peony.Planta. 2021 Sep 8;254(4):67. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03715-z. Planta. 2021. PMID: 34495419
-
Biogenesis of flavor-related linalool is diverged and genetically conserved in tree peony (Paeonia × suffruticosa).Hortic Res. 2022 Nov 7;10(2):uhac253. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac253. eCollection 2023 Feb. Hortic Res. 2022. PMID: 36751271 Free PMC article.
-
The Scent of Lily Flowers: Advances in the Identification, Biosynthesis, and Regulation of Fragrance Components.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 8;26(2):468. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020468. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the aesthetic secrets: exploring connections between genetic makeup, chemical, and environmental factors for enhancing/improving the color and fragrance/aroma of Chimonanthus praecox.PeerJ. 2024 Apr 19;12:e17238. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17238. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38650650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Traditionally Used Edible Flowers as a Source of Neuroactive, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Extracts and Bioactive Compounds: A Narrative Review.Molecules. 2025 Feb 4;30(3):677. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030677. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated physiological, microbial, and metabolomics analyses revealed the differences in different varieties of Paeonia lactiflora Pall.Front Plant Sci. 2025 May 23;16:1577695. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1577695. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40487213 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and volatile compounds analyses of floral development provide insight into floral scent formation in Paeonia lactiflora 'Wu Hua Long Yu'.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Feb 16;15:1303156. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1303156. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38434428 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the molecular secrets of Paeonia plants: advances in key gene mining and molecular breeding technology.Hortic Res. 2025 Apr 30;12(7):uhaf090. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhaf090. eCollection 2025 Jul. Hortic Res. 2025. PMID: 40352288 Free PMC article.
-
Flower morphology, flower color, flowering and floral fragrance in Paeonia L.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Nov 21;15:1467596. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1467596. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39640998 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang X., Wang C., Yao K., Zhang W., Yang L., Li C. Research progress of the device form of solid phase microextraction. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2017;03:55–58. doi: 10.13881/j.cnki.hljxmsy.2017.0206. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

