Plakophilin-3 Binds the Membrane and Filamentous Actin without Bundling F-Actin
- PMID: 37298410
- PMCID: PMC10253835
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24119458
Plakophilin-3 Binds the Membrane and Filamentous Actin without Bundling F-Actin
Abstract
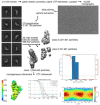
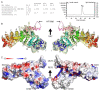
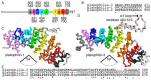
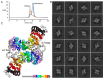
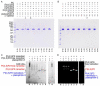
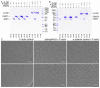
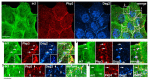
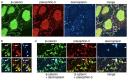
Plakophilin-3 is a ubiquitously expressed protein found widely in epithelial cells and is a critical component of desmosomes. The plakophilin-3 carboxy-terminal domain harbors nine armadillo repeat motifs with largely unknown functions. Here, we report the 5 Å cryogenic electron microscopy (cryoEM) structure of the armadillo repeat motif domain of plakophilin-3, one of the smaller cryoEM structures reported to date. We find that this domain is a monomer or homodimer in solution. In addition, using an in vitro actin co-sedimentation assay, we show that the armadillo repeat domain of plakophilin-3 directly interacts with F-actin. This feature, through direct interactions with actin filaments, could be responsible for the observed association of extra-desmosomal plakophilin-3 with the actin cytoskeleton directly attached to the adherens junctions in A431 epithelial cells. Further, we demonstrate, through lipid binding analyses, that plakophilin-3 can effectively be recruited to the plasma membrane through phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate-mediated interactions. Collectively, we report on novel properties of plakophilin-3, which may be conserved throughout the plakophilin protein family and may be behind the roles of these proteins in cell-cell adhesion.
Keywords: actin cytoskeleton; armadillo; desmosomes; phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; plakophilin; plasma membrane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The function of plakophilin 1 in desmosome assembly and actin filament organization.J Cell Biol. 2000 Apr 3;149(1):209-22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.1.209. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10747098 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitoylation of plakophilin is required for desmosome assembly.J Cell Sci. 2014 Sep 1;127(Pt 17):3782-93. doi: 10.1242/jcs.149849. Epub 2014 Jul 7. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 25002405 Free PMC article.
-
The head domain of plakophilin-1 binds to desmoplakin and enhances its recruitment to desmosomes. Implications for cutaneous disease.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 25;274(26):18145-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.26.18145. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10373410
-
Plakophilins: Multifunctional proteins or just regulators of desmosomal adhesion?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Jan;1773(1):69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.04.009. Epub 2006 May 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 16765467 Review.
-
Plakophilins in desmosomal adhesion and signaling.Cell Commun Adhes. 2014 Feb;21(1):25-42. doi: 10.3109/15419061.2013.876017. Cell Commun Adhes. 2014. PMID: 24460199 Review.
Cited by
-
Two δ-Catenins, Plakophilin 4 and p120, Promote Formation of Distinct Types of Adherens Junctions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 15:2025.06.14.659701. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.14.659701. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40661375 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

